Have you ever taken a photo or video and noticed it looked blurry or shaky? This is often because of camera shake, which happens when the camera moves slightly during the shot. To solve this problem, camera manufacturers have developed technologies like Image Stabilization (IS) and Vibration Reduction (VR). Let’s dive into these technologies and understand how they help capture clear and sharp images.

What is Camera Stabilization?
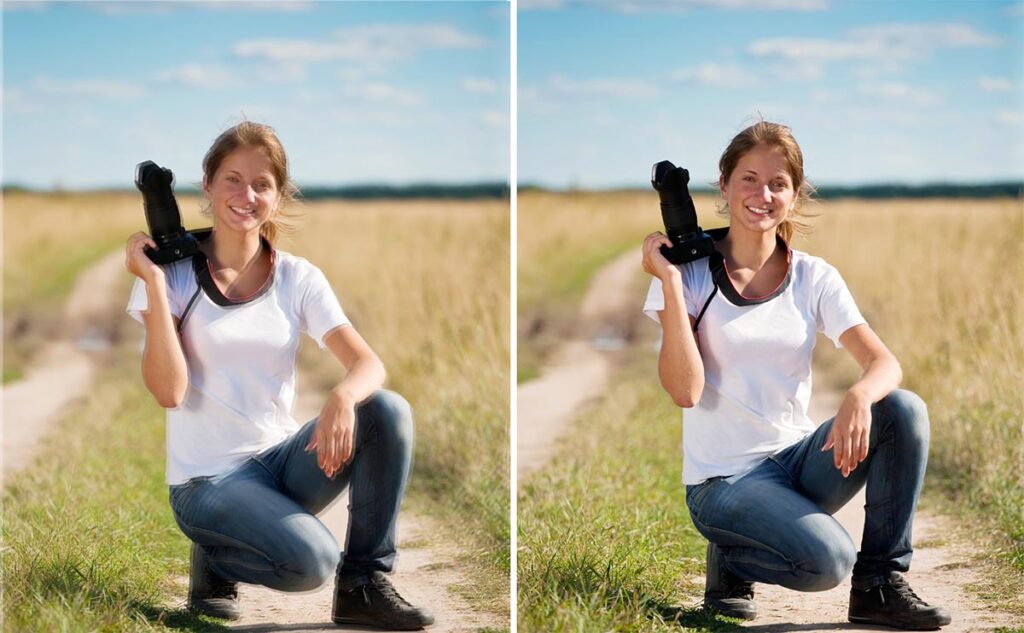
Camera stabilization refers to techniques and technologies used to keep the camera steady while taking photos or videos. By minimizing unwanted movements, stabilization ensures that images are sharp, and videos are smooth. This is especially important in low-light conditions or when using zoom lenses, as even small movements can cause noticeable blur.
While the stabilization concept is exactly the same across every lens brand. Different names for Optical Stabilization include:
- Canon – Image Stabilization (IS)
- Nikon – Vibration Reduction (VR)
- Sigma – Optical Stabilization (OS)
- Tamron – Vibration Compensation (VC)
- Leica – MegaOIS
- Pentax – Shake Reduction (SR)
Types of Camera Stabilization
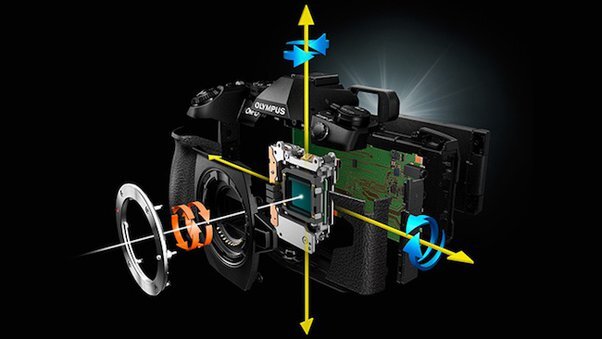
1. Optical Image Stabilization (OIS):
- How it works: OIS involves tiny motors or actuators inside the camera lens or body that move elements to counteract camera shake. When the camera detects movement, these elements shift in the opposite direction to keep the image stable.
- Benefits: OIS works well for both photos and videos, providing steady shots without affecting image quality.
2. Digital Image Stabilization (DIS):
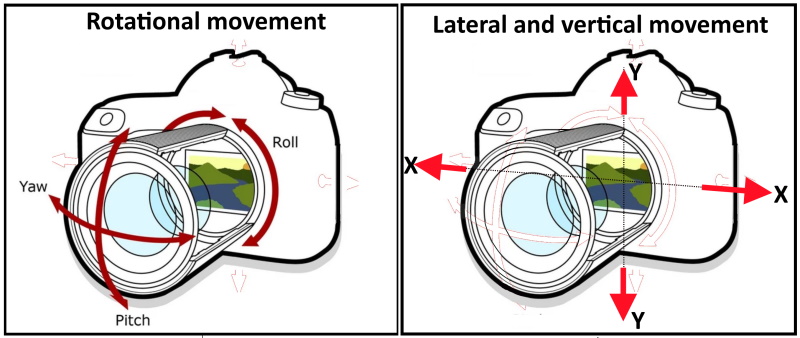
- How it works: DIS uses software algorithms to reduce shake after the photo or video is captured. The software analyzes the movement and adjusts the image to compensate.
- Benefits: DIS can be helpful, but it might slightly crop the image and can be less effective in very shaky conditions.
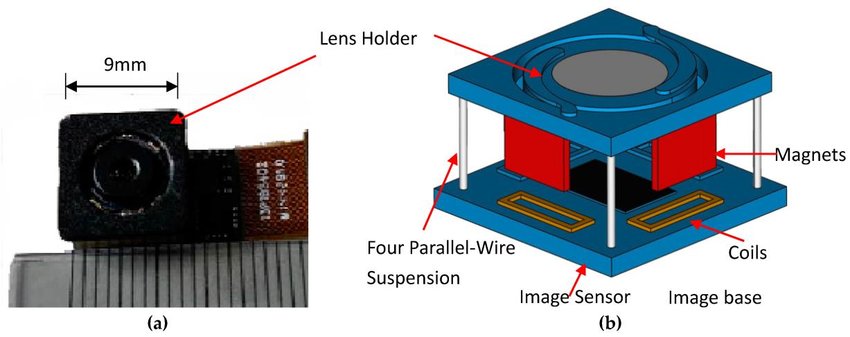
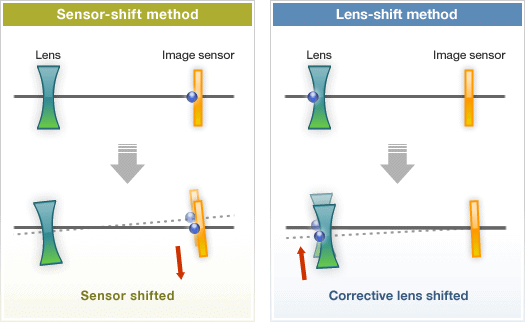
3. Sensor-Shift Stabilization:
- How it works: This method moves the camera sensor itself to counteract movements. The sensor adjusts its position based on the detected shake, keeping the image steady.
- Benefits: Sensor-shift stabilization is effective for both photos and videos and works with any lens attached to the camera.
4. Lens-Based Stabilization:
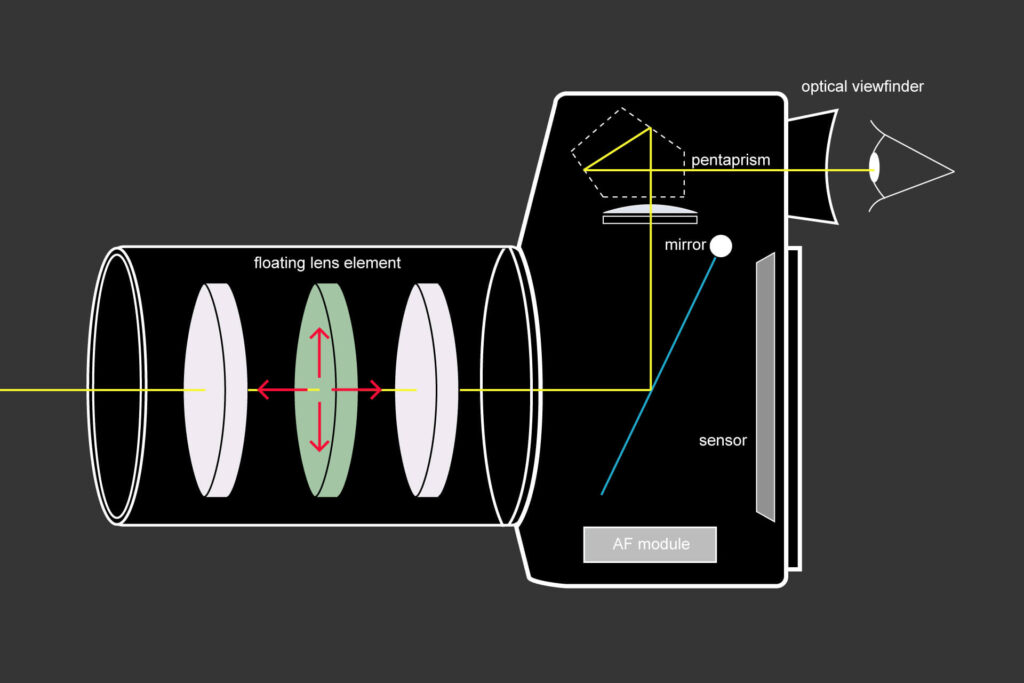
- How it works: Similar to OIS, this method involves moving lens elements. It’s usually found in interchangeable lenses for DSLRs and mirrorless cameras.
- Benefits: Lens-based stabilization is highly effective and tailored to the specific lens, providing excellent results.
5. Gimbals:
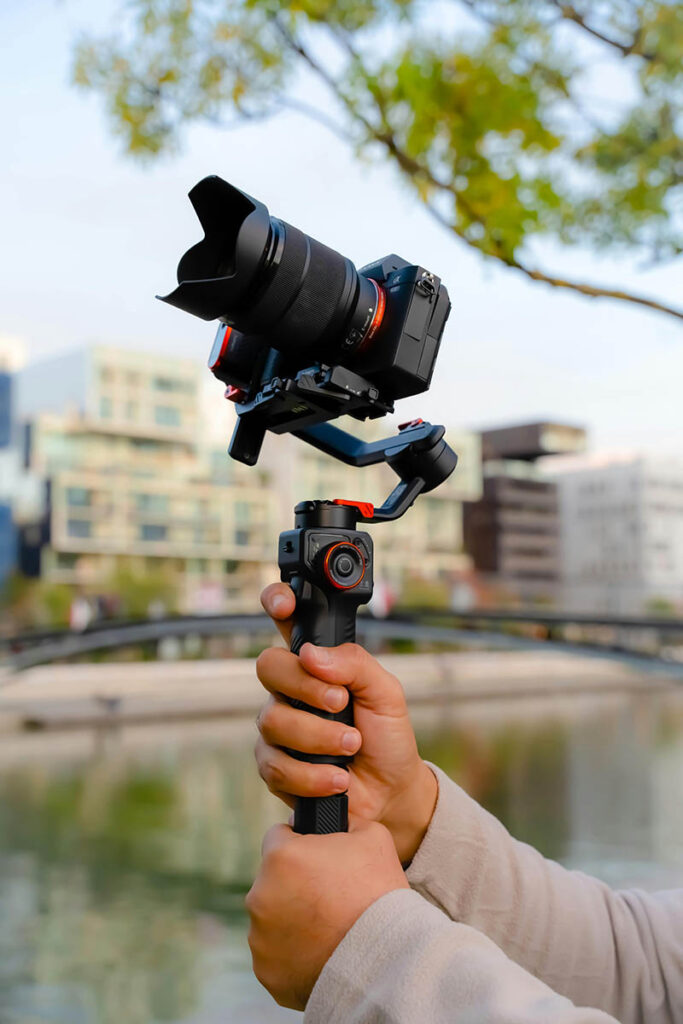

- How it works: Gimbals are external devices that hold the camera and use motors to keep it balanced. They can be handheld or mounted on drones.
- Benefits: Gimbals are excellent for video, providing very smooth and professional-looking footage even in dynamic movements.
Why is Camera Stabilization Important?
Practical Tips for Using Stabilization
1. Turn it on: Ensure the stabilization feature is activated in your camera settings.
2. Use a Tripod: For maximum stability, especially in very low light or when using a long exposure, use a tripod. (Note: When you use tripod, do not forget to switch off the image stabilization of the lens. Otherwise, it makes unwanted jerks and makes image blurry.)
3. Handheld Tips: Keep your elbows close to your body and use both hands to hold the camera.
4. Gimbals for Video: If you shoot a lot of videos, consider investing in a gimbal for the smoothest footage.
Conclusion
Camera stabilization, whether through OIS, DIS, sensor-shift, or gimbals, plays a crucial role in modern photography and videography. It allows photographers and videographers to capture clear, sharp, and smooth images and videos in various conditions. By understanding and utilizing these technologies, you can significantly improve the quality of your shots and create stunning visual content.