Do you know how camera works? I am starting with D-SLR. The full form of D-SLR is Digital Single Lens Reflex. Hence the signal helps to capture light digitally. There are two types of signals available to convey information from one area to another. So, the question arises why digital?
Data and Signal
Signals are the electric or electromagnetic impulses used to encode and transmit data. Data is then transmitted through some medium, such as a cable or the airwaves. The receiving node then reverses the conversion and turns the electronic pulses or waveforms back into the 0’s and 1’s that represent the original data.
Analog Signal
An Analog signal is a continuous flow. It produces a smooth and continuous curve. It produces a more accurate representation of changes in physical phenomena such as sounds, light, temperature, pressure, etc. analog communication system is less sensitive in terms of electrical tolerance.
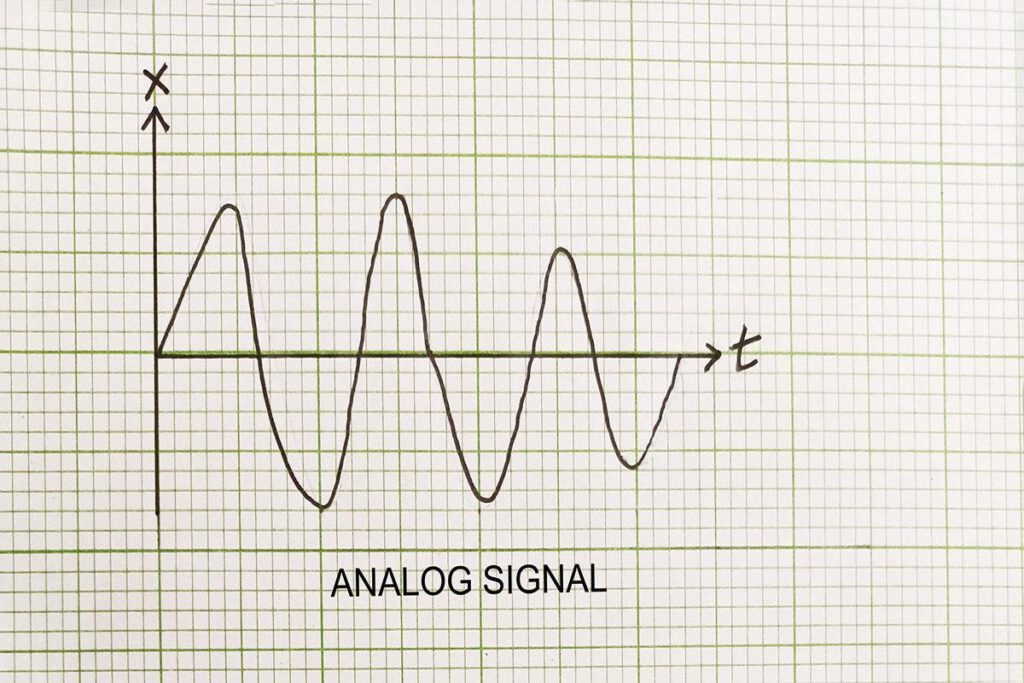
Digital Signal
The digital signal flows discretely. It takes one value from a finite set of possible values at a given time. It includes a limited variety of values which lies between 0 and 1. It is much more advantageous than an analog signal.
Therefore, the continuous signal or analog is less resistant to the noise. It generates more distortion of the digital signal.
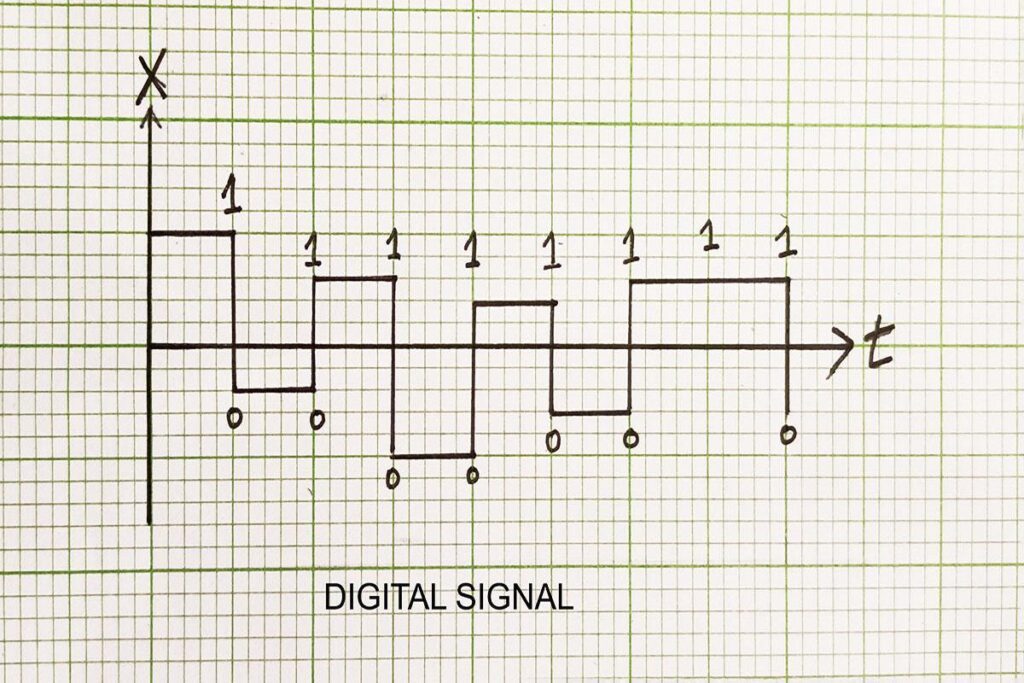
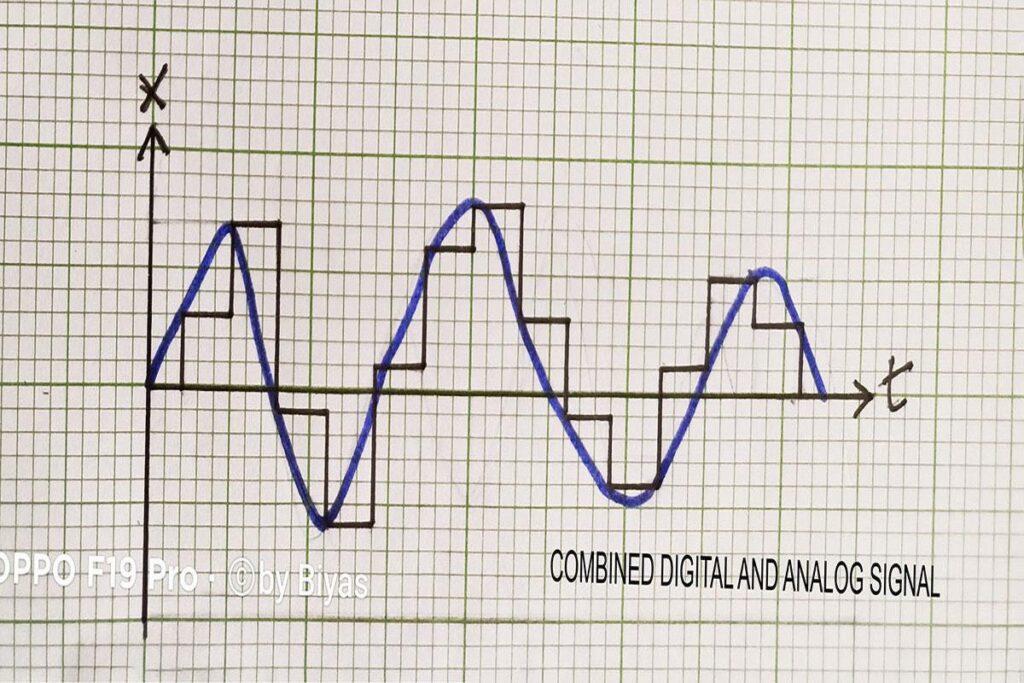
The merits of the digital signal are as follows :
- Digital signal transfer data in a wide range.
- Distinct values in a limited set 0 and 1.
- The calculations and algorithms run more accurately with a square wave.
- Signal is always positive.
- It is encrypted.
- It requires higher bandwidth.
- It stores data in binary bit form.
- It resists noise throughout the transmission devoid of any deterioration.
- It requires less power than an analog signal.
- Transmission rate is higher than an analog signal.
- Digital signals are mainly used in digital electronic devices like computers, PDS, cell phones, and DSLR cameras.
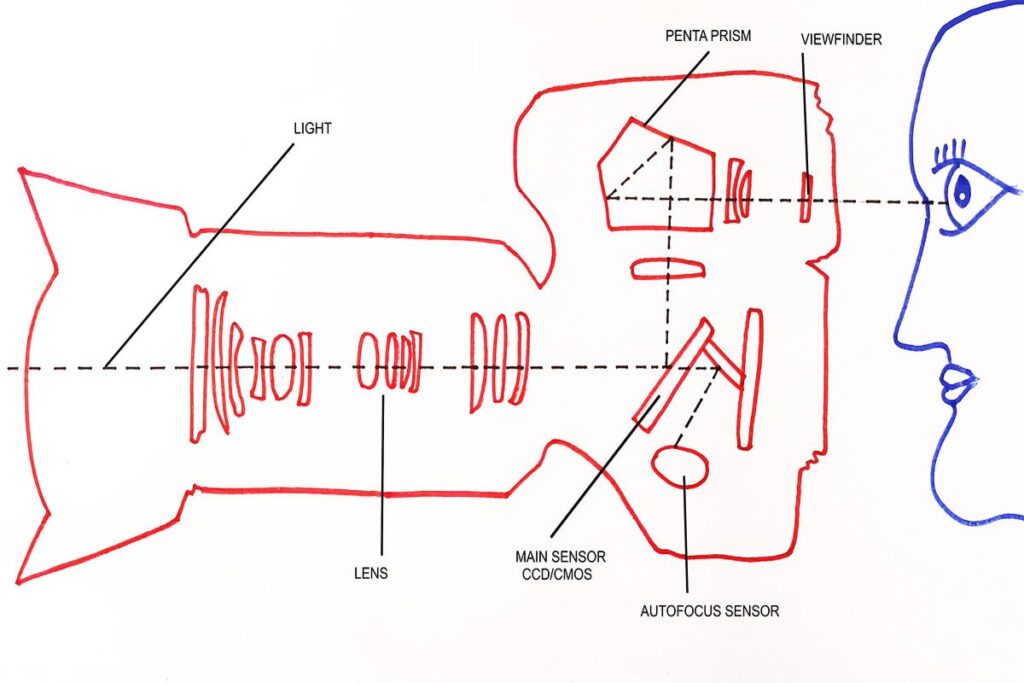
Mechanism of D-SLR Camera
The reflected light from an object directly hits the lens of the camera and goes to the image sensor. A mirror is fixed in front of the image sensor. It captures the reflection at a 45-degree angle of light and forwards vertically to the pentaprism.
The pentaprism then converts the vertical light to horizontal by redirecting the light through two separate mirrors, right into the viewfinder. It helps the photographer to capture the same image that he sees from the viewfinder. When he releases the shutter button, the mirror swings out of the way and the image captures in the digital image sensor.

The image processor sends data (picture file) in an appropriate format (.NEF or .jpeg/.jpg). The SD (Secure Digital) card helps to store the image (reflected light) permanently. The whole process takes very little time. Some professional DSLR cameras can store 11+ pictures in a second.
Focusing system – masked basics of photography
Image sensor and autofocus (AF) sensor are different. They are placed in different places in DSLR camera body. The reflected light hit the mirror of DSLR camera body and most of the light hit to pentaprism. That light goes to the viewfinder from pentaprism. Some light goes through a semi-transparent area of the main mirror to the secondary mirror. It goes down to the auto focus (AF) sensor.

The advanced technology installs a tiny motor in camera body or lens to move forward or backward of the focusing element of group from the image sensor. It turns the image sharp. The autofocus camera needs to calculate focus electronically as the lens moves to and from the sensor.
Active focus system
At present, you couldn’t find the active focus system. In earlier days, this system helps to focus automatically. It was transmitted an ultrasonic or infrared signal toward the subject. The subject reflected light straight to the camera sensor at the speed of light (1,86,000 miles/second or 3,00,000 kilometers per second). So, the camera focus system easily detected the image distance from its sensor. You can call it sonar or radar of the camera system.
AF-Assist Lamp on your DSLR camera is not the part of the focus system. It only assist camera focus sensor to give more light in darker situation. It is under the passive focus system.
Passive Focus System
It determines the distance to the subject by various algorithms like Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), Morphology, Self-organizing map (SOM) neural network. It computes the perfect reflection by using the surrounding light environment to analyze it and then deciding where to focus for the sharp image. Passive Focus system is divided into two distinct systems.
a) Phase Detection – masked basics of photography
As we know that the major reflected light directly enters into the angled mirror through lens. The light goes directly to the pentaprism vertically and then it comes to the view finder horizontally. The reflected light of the subject from mirror goes down to the autofocus sensor. Previously there was only one image sensor.
Now-a-days there are couple of image sensors are available in the microcomputer. Therefore, more than one image is created for every sensor in phase detection. Now the images are compared and their positional relationship evaluated. The microcontroller commands the lens to do the focus until and unless the images are identical. When the images are identical then the subject is in sharp focus. The AF sensor done these total jobs within millisecond.
Every sensor is evaluated vertically. Therefore, image sensor struggles for perfect focus of the horizontal components of subject. At present, the cross type points (both vertical and horizontal) helps to focus much faster and accurate.
b) Contrast Detection – masked basics of photography
This system is mainly used by point and shoot camera, DSLR camera live view, smart phones and mirrorless DSLR camera. The name contrast detection is self descriptive. It analyze the contrast of a subject in a repetitive process. The main image sensor record the contrast, hence, the focus is more accurate by eliminating mechanical misalignment. It is a continuous process.
You can find contrast detection even in your DSLR camera with mirror. The live view mode runs with same technology because mirror locked up and main image sensor detect the contrast of image in a repetitive process.

The electronic circuit analyze the most contrast reflection with the previous image contrast taken and derived the accurate focus. The main problem arise when the AF sensor detect the optimum contrast but doesn’t take decision whether it is perfect focus or not. Therefore, a gradient method is followed by contrast detection. It is also called “Hill Climbing” method.
If we draw a curve based on image contrast, he peak may be the highest contrast. But sensor invites another contrast and analyze. If the contrast decreases, the contrast detection system changes the direction toward the highest or peak point. It is a continuous process until and unless the peak contrast found.
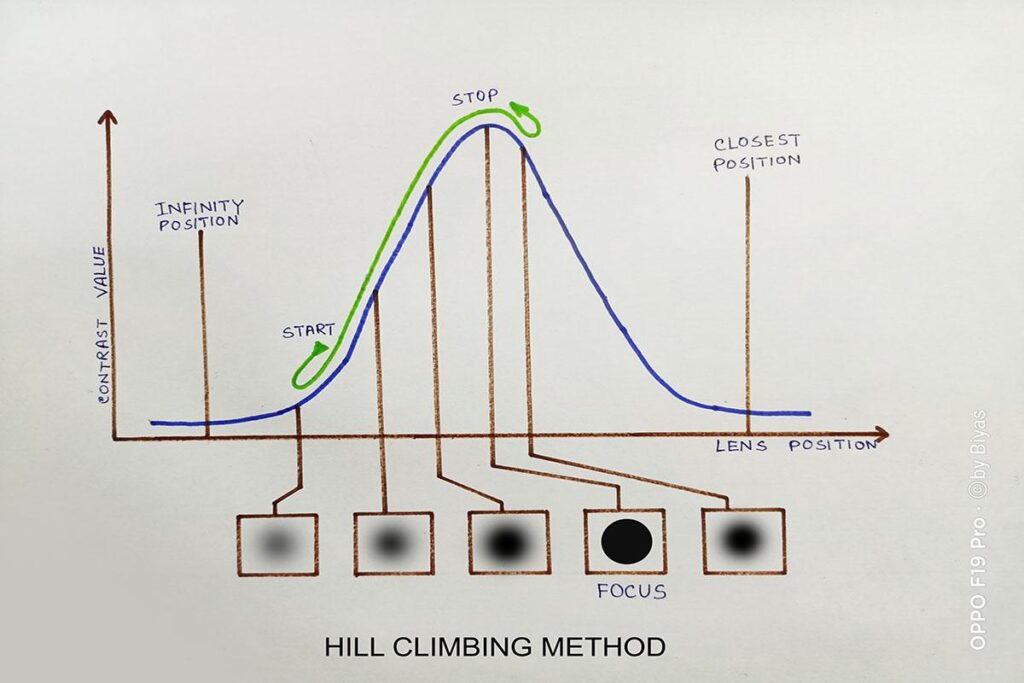
This technology is inexpensive than the phase-detection system. It gives perfect results in portrait photography to select the eye of the subject. But if you are a wildlife photographer or stage/concert photographer to cover a dance programme, contrast detection runs slower. The AF tracking and continuous focus abilities of your camera give better results with phase detection.
In contrast detection system, there is no other AF sensor. Hence, the production cost is reduced. It doesn’t force any calibration error like front or back focus in phase detection.

On the other hand, it never measure distance between the subject and sensor. So, the contrast detection is slower. Speed decreases in low light and low contrast. It encourages increasing noise as constant illumination of the image sensor. It also generates heat more than phase detection system.
Image sensors
There are two types of images sensors available. Both use the photoelectric effect to convert photons into an electric signal. Albert Einstein described photoelectric effect in 1905 based on Plank’s hypothesis. He proposed that light was made up of particles with energy related to the frequency of the light.
Photoelectric Effect by Einstein based on Plank’s hypothesis
E = hv where E=energy, h = Plank’s constant (h=6.626 x 10 ^ -34 Joules) and v = frequency. Here v is the Greek letter nu. It is not English letter v. It is all about Quantum theory.
Once a photoelectron is created it needs to capture and quantify. CCD and CMOS capture, quantify and recreate the image. Both CCD and CMOS sensors are formed by a matrix of pixels. Each pixel is a light sensitive area where the photoelectric effect takes place, but once the photoelectron is confined within the pixel, CCDs and CMOS treat it completely differently.
Charge Coupled Device [ CCD ]
A typical autofocus sensor is a charge coupled device (CCD). It is an array of photodiodes. It looks like a large dot filled grid. Each of these dots is a light receptor, called photodiode. The quantum efficiency is very high which helps to get the perfect focus in very poor light.
Light from the subject hits the array of pixels and the microprocessor note the value from each pixel. CCD converts light into electrons. It is an analog device which is immediately converted to a digital signal by an analog to digital converter.
CMOS
The full form of CMOS is Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor. This sensor is a digital device. It converts charge (CCD) from a photosensitive pixel to a voltage at the pixel site. This signal is multiplexed by row and column to multiple on chip and digital to analog converters. CMOS sensors have high speed, low sensitivity and fixed pattern noise. It consumed less power (100 times less than CCD), lower price than CCD and smaller size.
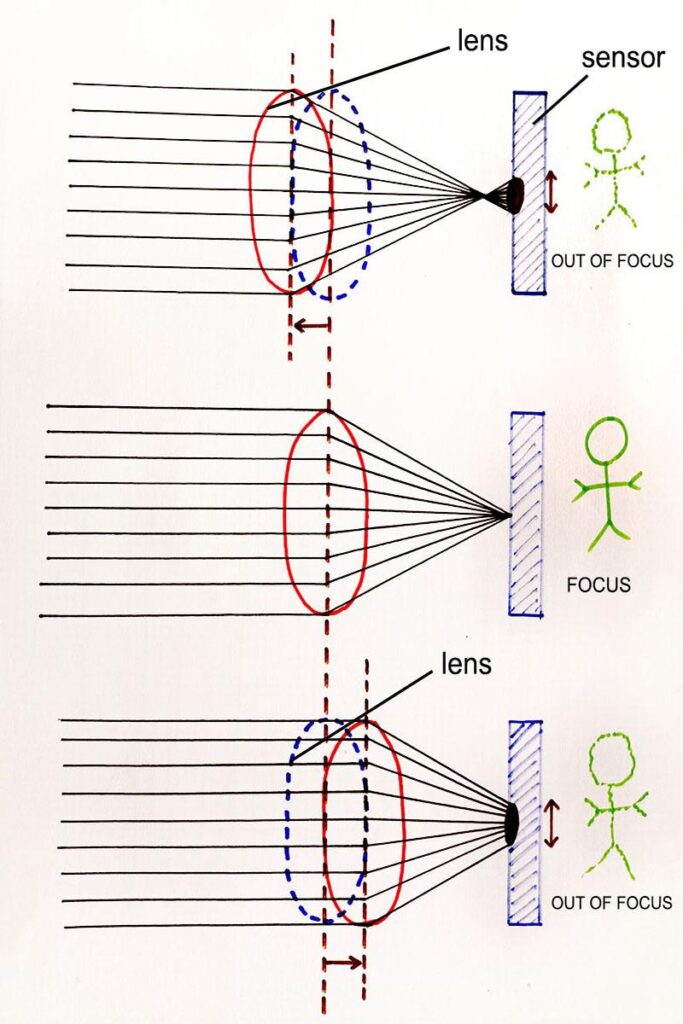
Hybrid Autofocus system – masked basics of photography
It generally starts to record image with a phase detection AF method. It then uses contrast detection AF system to refine the edge. The phase detection already detect the focus point, contrast detection does not take the normal time it would taken.
Sony a6500 is a hybrid AF DSLR with 0.05 second.
Read more:
Masked basics of photography part II
Masked Basics of Photography Part III
Masked basics of photography part IV
Acknowledgement: Nandita Chakrabarti, Math, Jordan Bergendahl, Thirdman and Karolina Grabowska

wow great article. lot to learn. thank you.
Class sir
Excellent
Baba khuub sundor hoyeche tomar website. ami sabaike bolbo tomar website dekhte.
Excellent