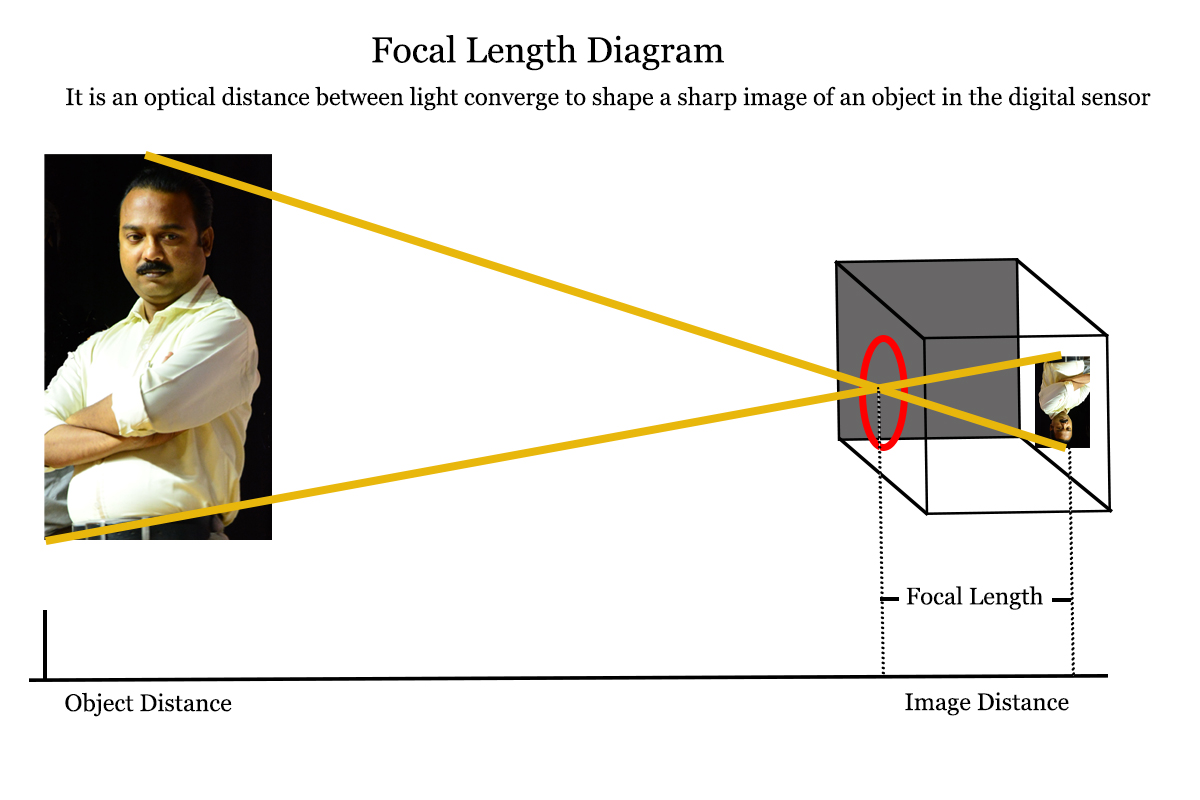
Focal length – basics of photography
Let’s unmask the hidden basics of lens which helps you to understand better about the distance of lens and sensor. It is an optical property of the lens. It is the distance between the lens and image sensor when the subject is in focus. The distance is measured in millimeter (mm). For example, 50 mm, 100 mm, 200 mm and so on. In the lens body it is clearly written. The prime lens has a fixed focal length (50 mm, 85 mm, 100 mm etc.) and zoom lens focal length varies like 18-55mm, 55-200mm, 70-300 mm etc.
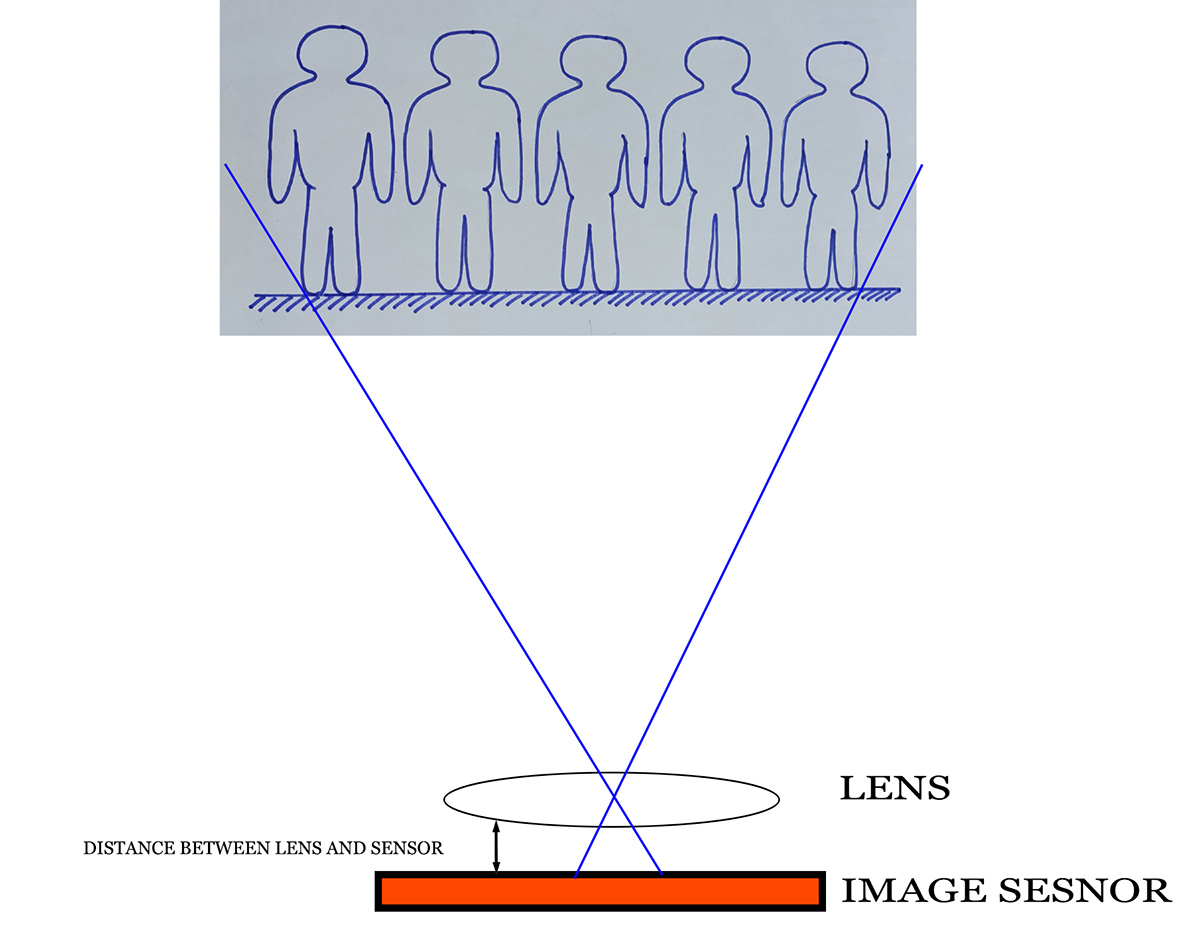
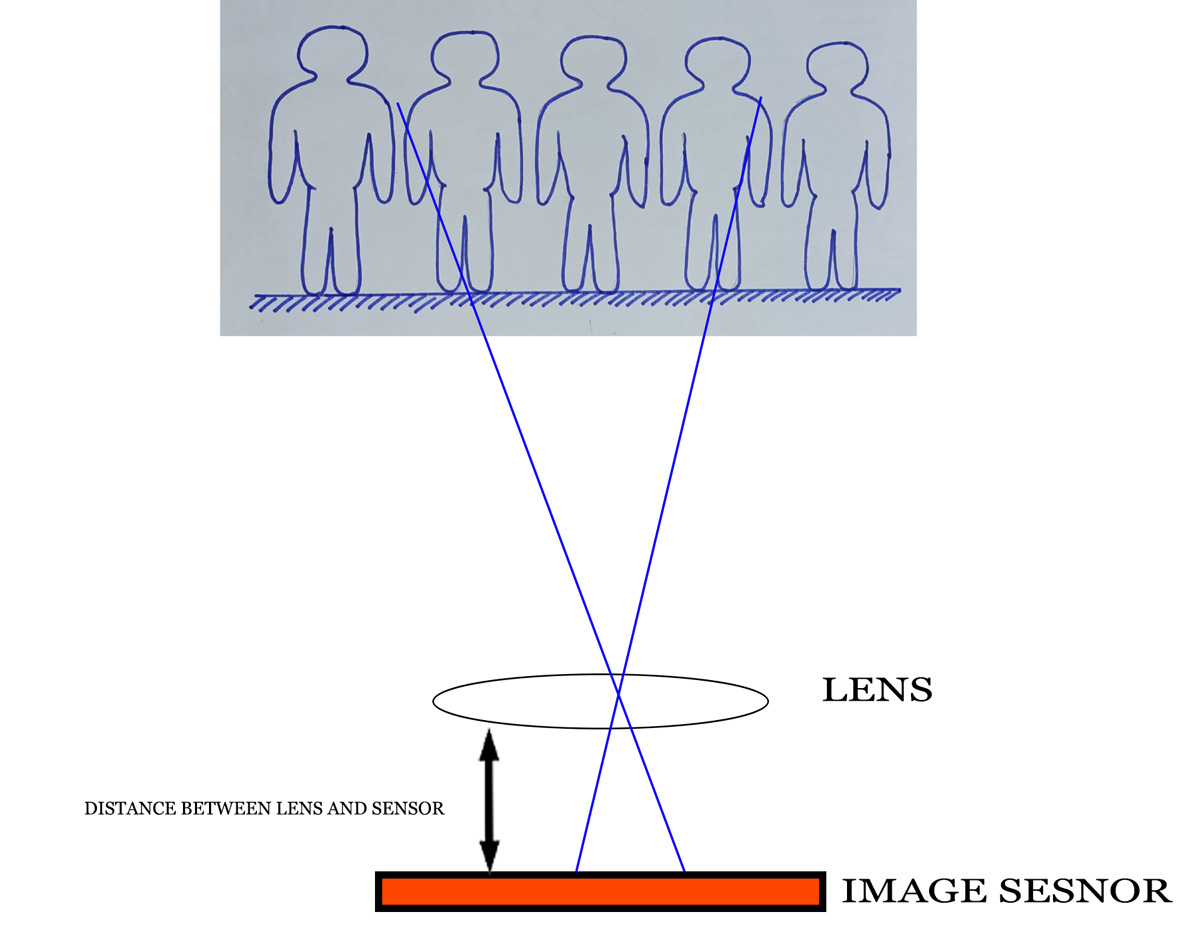
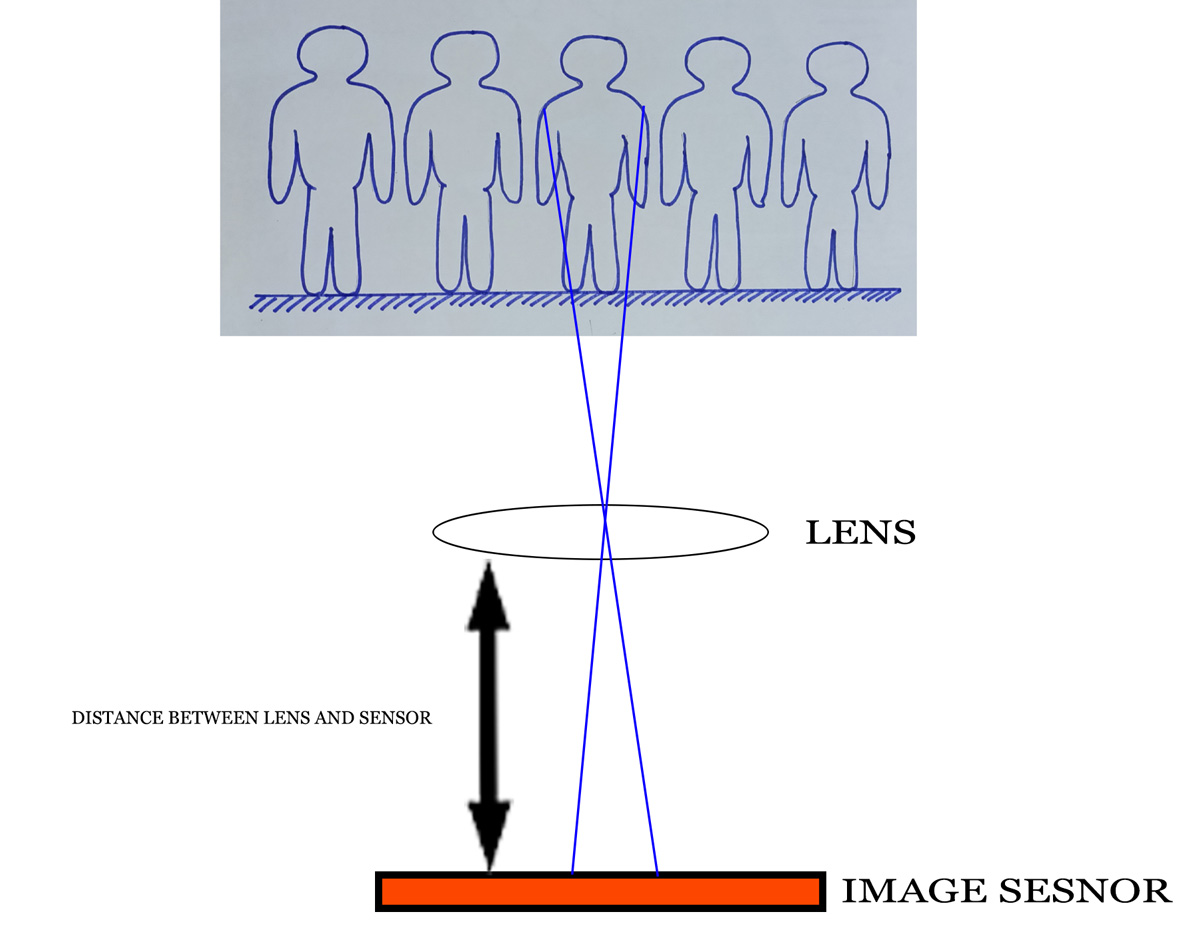
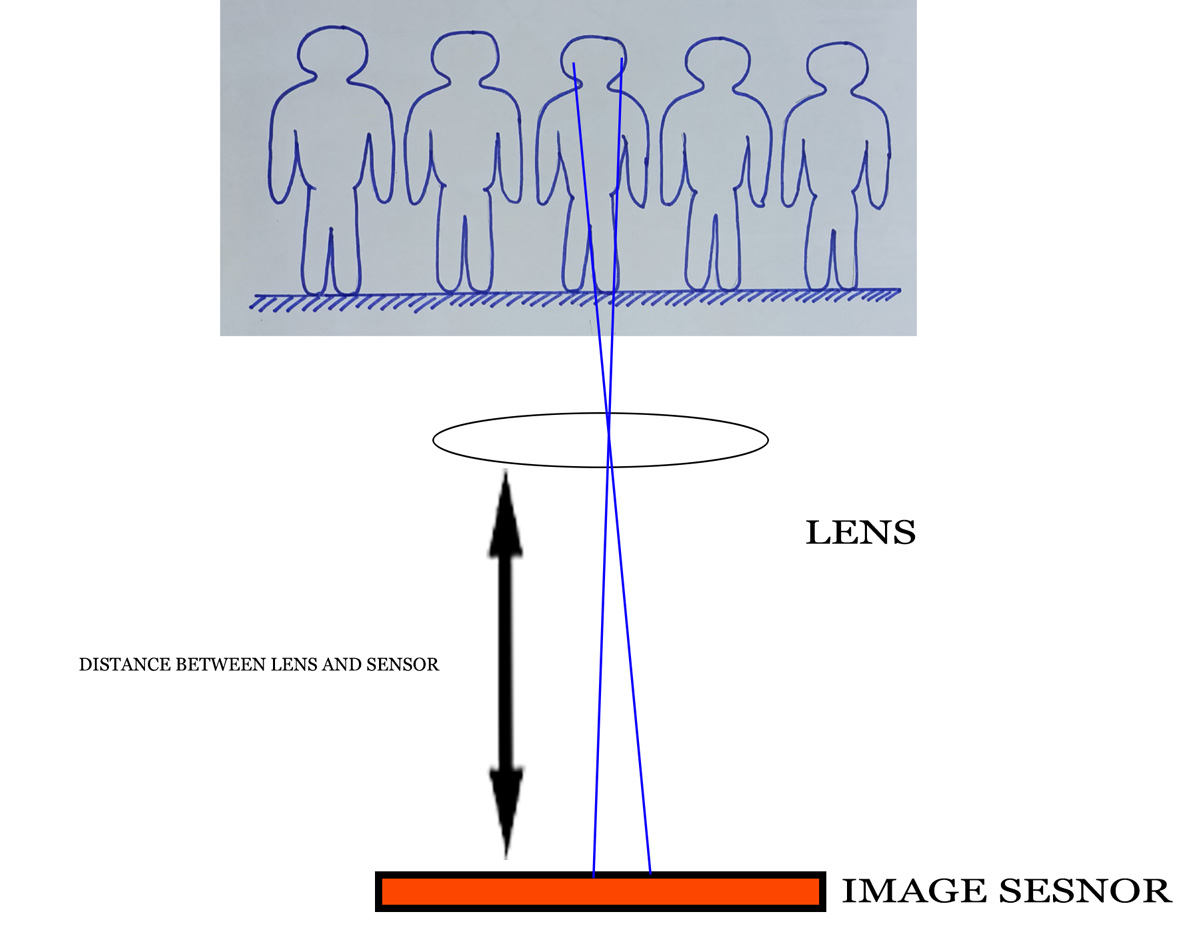
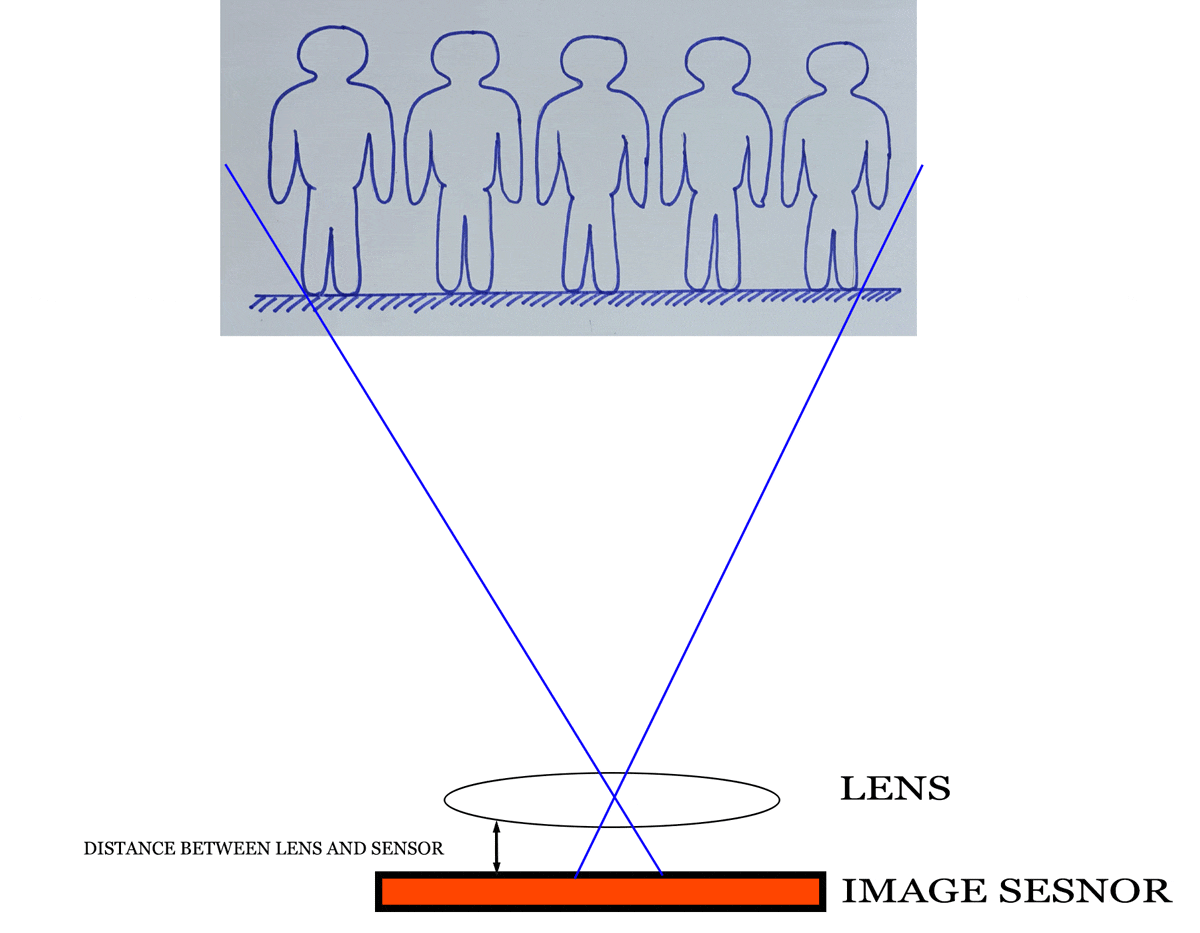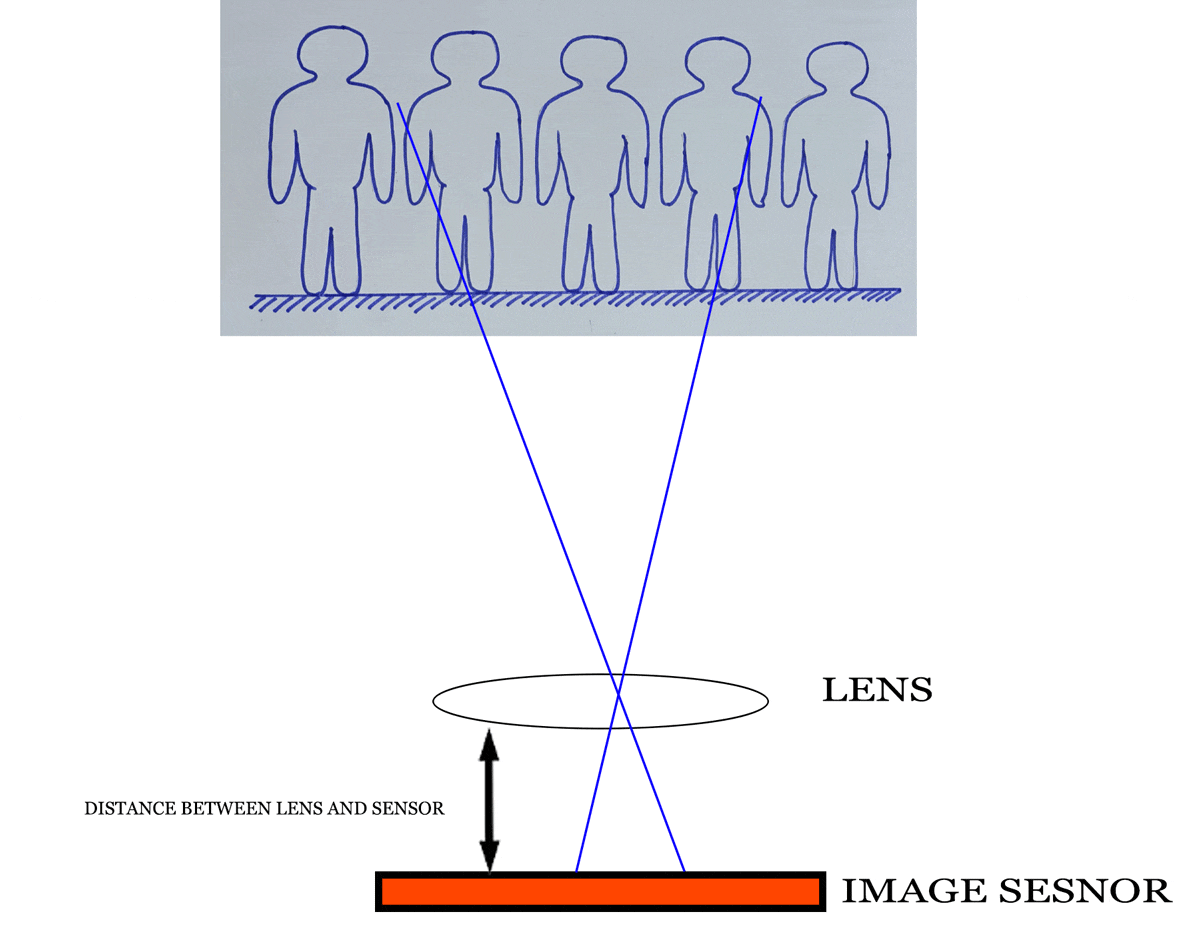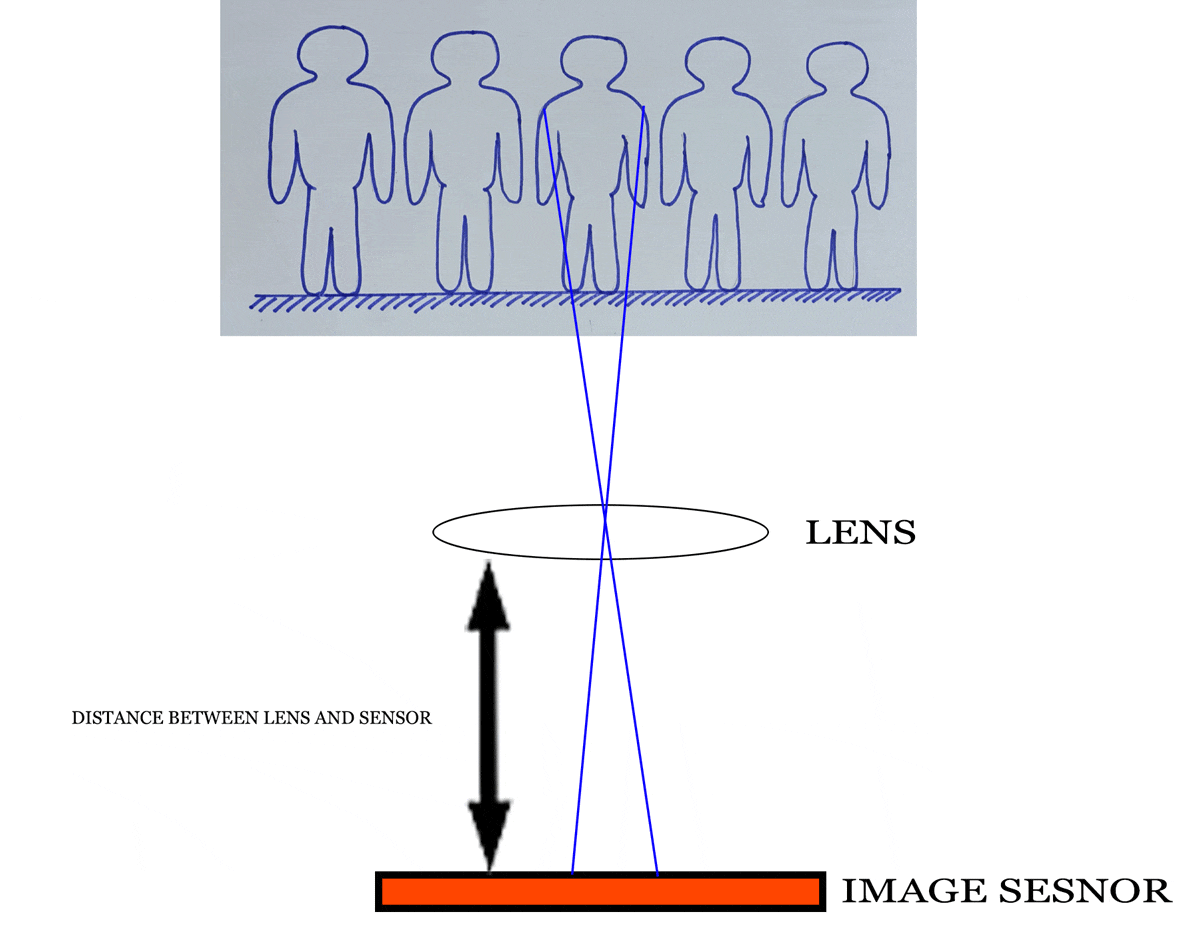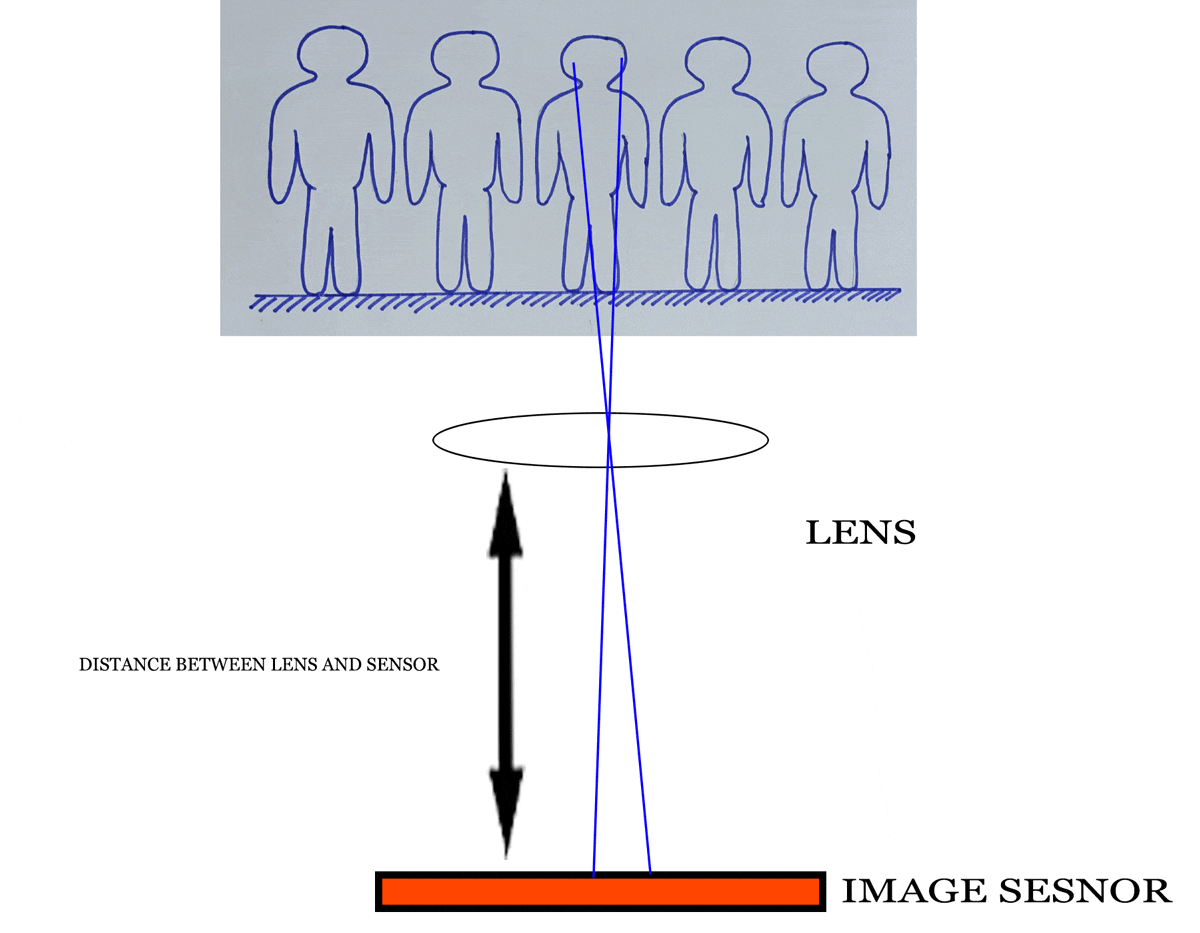
Focal length is keenly related with angle of view. Sometimes it is known as Field of View (FOV) or lens view. I think you know the viewfinder is in a rectangular shape. It is true for the image sensor shape also. So, horizontal and vertical and diagonal angle of view will be different.
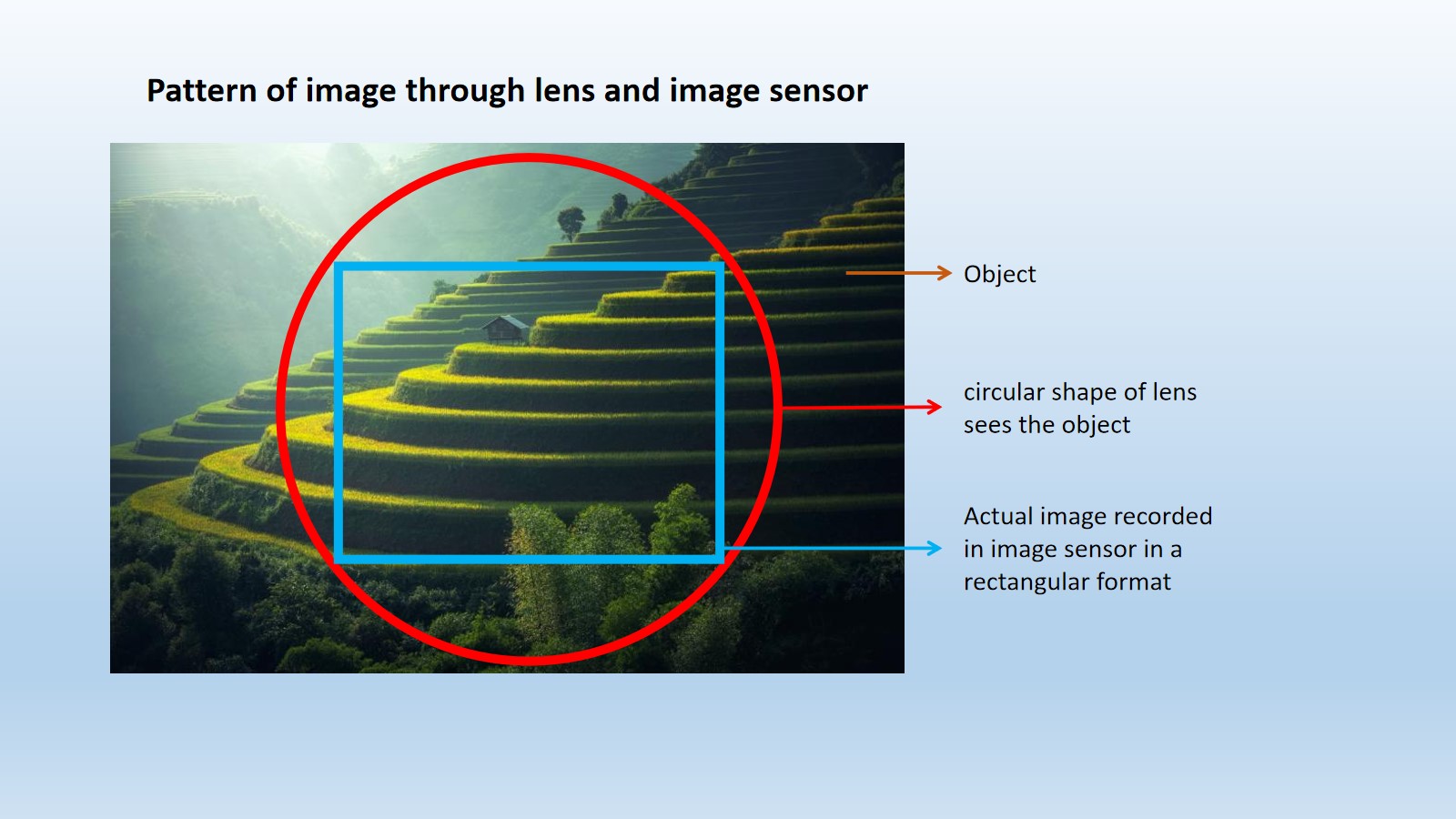
Image template on lens and image sensor
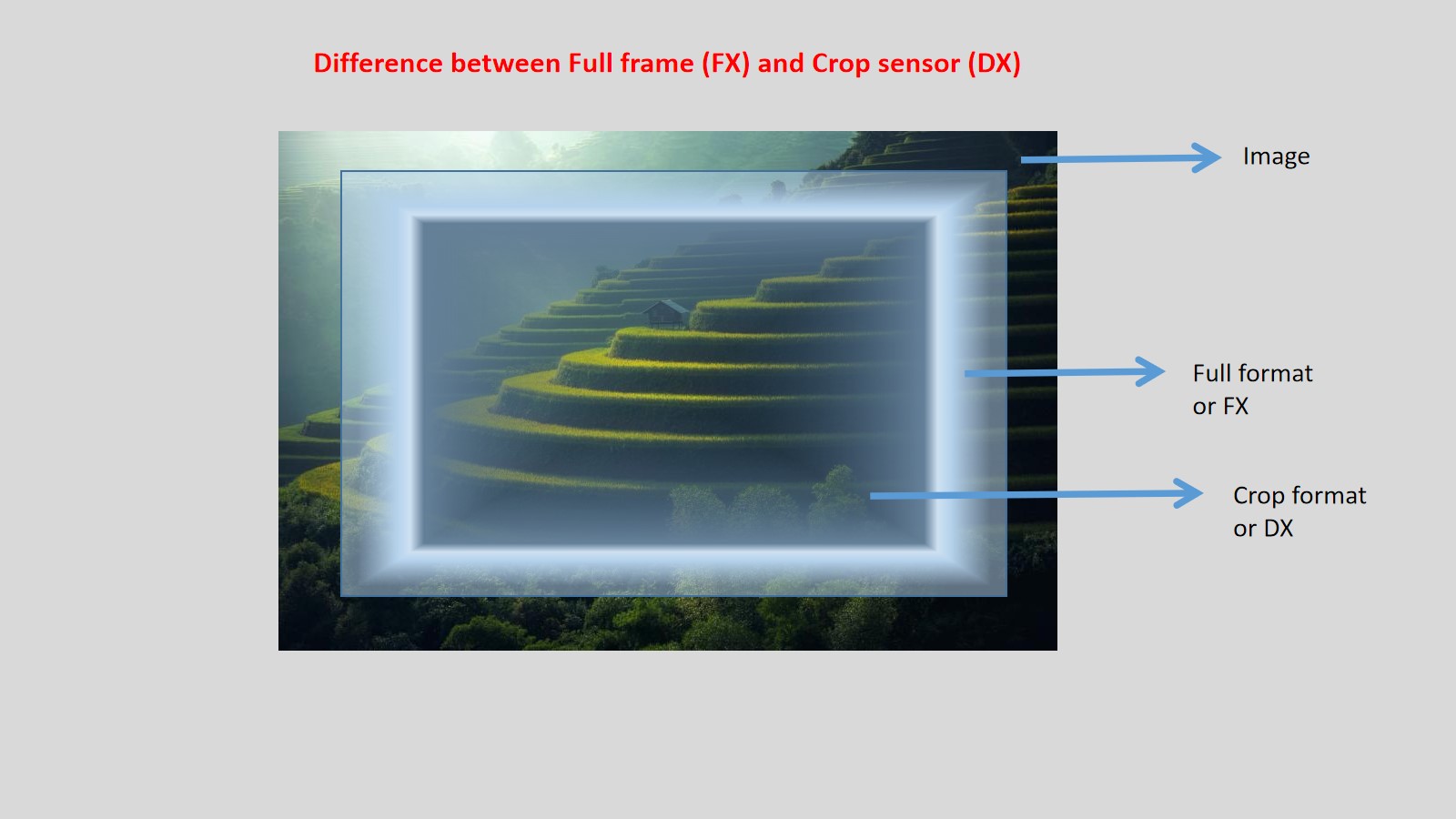
Again, unmask the hidden elements of photography. When a lens sees your stunning composition, it is a circular pattern. Because the lens is a round shape. When the image falls into the image sensor then the rectangular image of your composition is recorded. Some areas of the image which is observed by the lens are subtracted.
Full frame and crop sensor
In past days SLR cameras used 35 mm films ( 36 mm x 24 mm). This is the ideal size till date in digital era also. Based on 35 mm size the D-SLR image sensors are manufactured. The complex techniques, algorithms with 35 mm format image sensor is very much costlier in the photography market. A tiny image sensor which is less than 35 mm size cuts the price of D-SLR camera. It is known as crop sensor. Therefore, a D-SLR camera is much more affordable to us.
Crop sensor size based on 35mm film size
Canon APS-C sensor size: 22.2 mm x 14.8 mm
Sony, Pentax, Fujifilm and Nikon sensor size: 23.5 mm x 15.6 mm to 23.7 mm x 15.6 mm
Note
If you have a crop sensor compatible lens, check it carefully whether it is tagged with APS-C format or not. The full form of APS-C is Advanced Photo System – Classic. Most crop sensor D-SLRs use the APS-C format, which is a 3:2 ratio, as is full frame, but approximates the size of Advanced Photo System Classic film, which is closer to 24mm rather than 35mm. Full frame size is 36mm x 24mm. It was popular in the 90s in point-and-shoot cameras. In the digital age, APS-C sensor cameras occupy a formidable presence among pros and amateurs alike.
The D-SLRs from the above companies with 35 mm format (36 mm x 24 mm) is known as full frame camera. Hence, the crop factor is 1. If you multiply 35 mm format with 1, it will be remained same.
The crop sensors which are less in size against 35 mm size have a crop factor of 1.5 or 1.6. Nikon crop factor is 1.5 and Canon crop factor is 1.6 for DX format camera. It is also known as crop sensor camera.
Let’s calculate the focal length of full frame and crop sensor
As you already know that the full frame format size is 36mm x 24mm and the crop sensors eliminate some portions of the image which is visible to full frame format D-SLRs.
Nikon uses crop factor 1.5
If the subject focal length is 300mm
Full frame: 300mm x 1 = 300mm
Crop sensor: 300mm x 1.5 = 450mm
Canon uses crop factor 1.6
If the subject focal length is 300mm
Full frame: 300mm x 1 = 300mm
Crop sensor: 300mm x 1.6 = 480mm
Knowledgebase
The digital zoom works in same algorithm. When you use telephoto lens and try to capture a far sighted object into nearer one, the digital zoom crop the image internally and it store the image with a narrower angle on the image sensor.
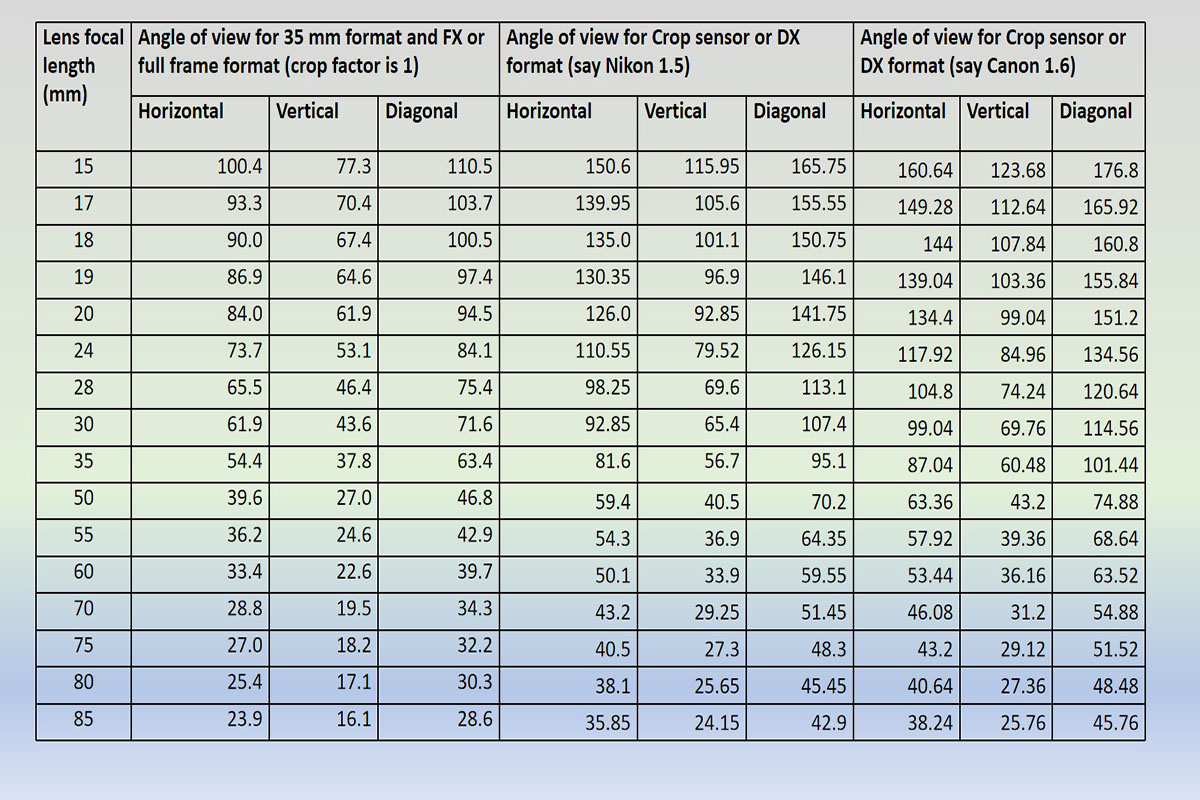
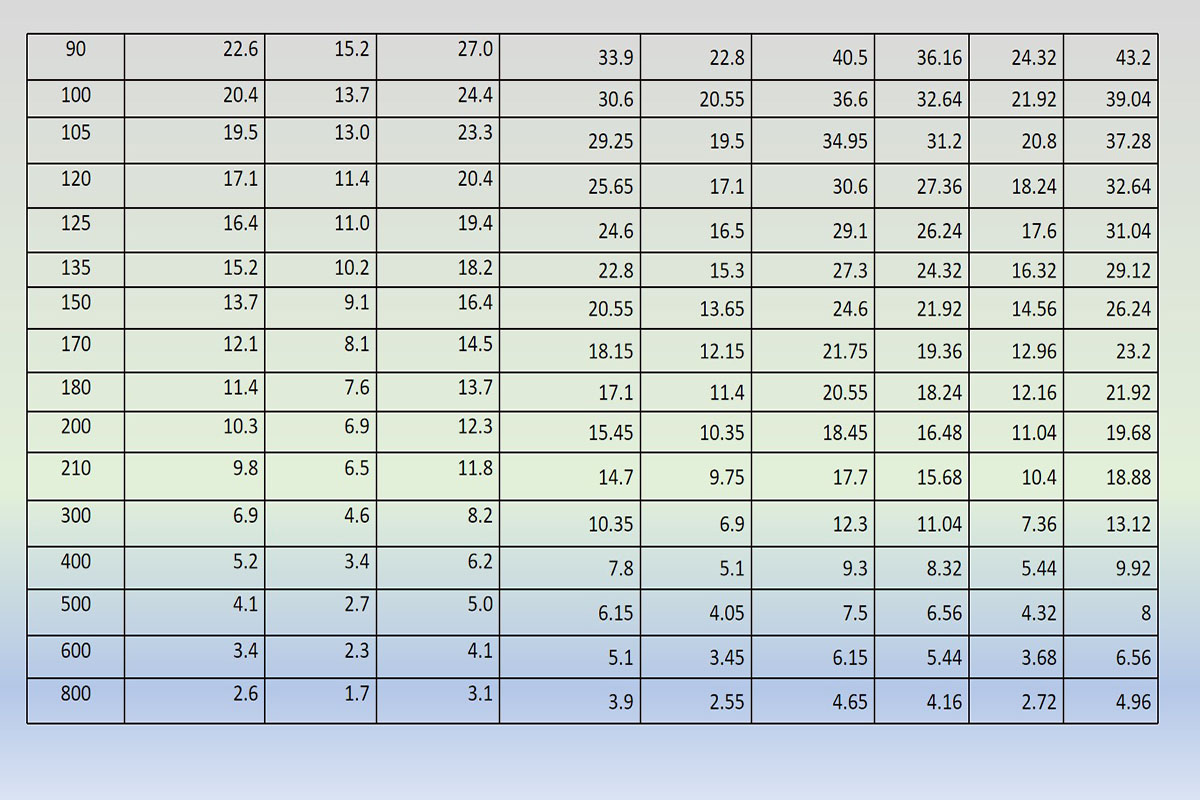
Relation between angle of view and focal length of lens
The crop factor creates an illusion of zoom in or apparently much bigger image. The algorithm works here to eliminate full frame (35 mm) size into small size (24 mm). The angle of view or Field Of View (FOV) runs much narrower and fills the image sensor. Therefore, you feel the image is in much more zoom in or enlarged.
Eyeglass and Lens
The lens are mainly used for the correcting the human sight error. The lens is mainly used for getting the proper focus object. Both concave and convex lens are used for correcting the blurry image. Concave lens is used for correcting nearsighted. Convex lens is used for correcting farsighted. A concave lens in front of the eye reduces the refraction of light and increase the focal length. Hence, the razor sharp image falls on the retina.
Convex lens is used in human eye where the eye’s lens and retina length are very short. So, the image is formed beyond the retina. To eliminate the problem, convex lens increase the refraction and reduce the focal length and a perfect image is created on the retina.
Working mechanism of telephoto lens and zoom lens
Galilean telescope invented by Galileo in 17th century. He combined a single convex lens with a concave lens. It enabled the distant object more visible and clear. So, the light condensed for convex and and refracted into parallel light into concave lens.
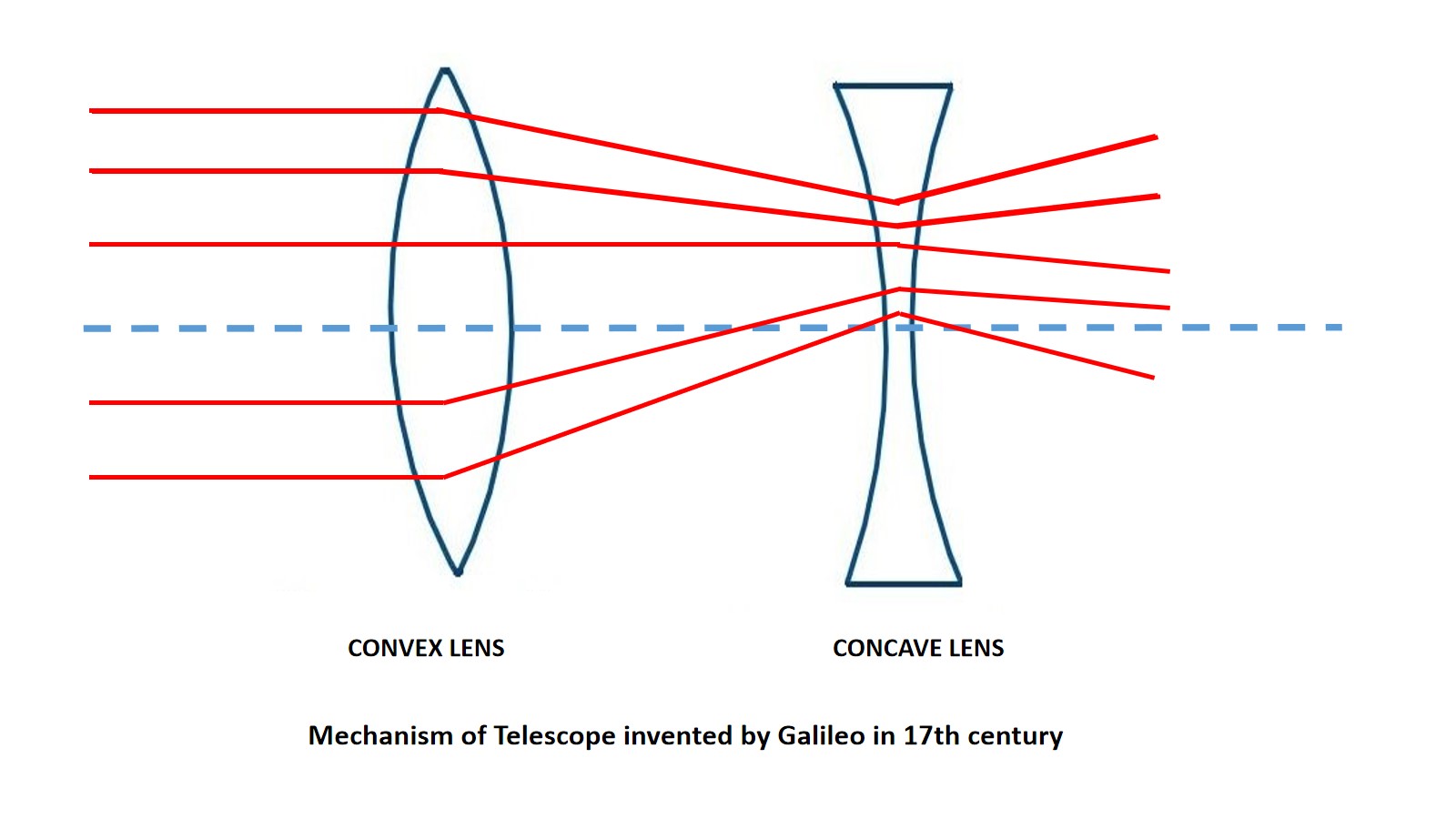
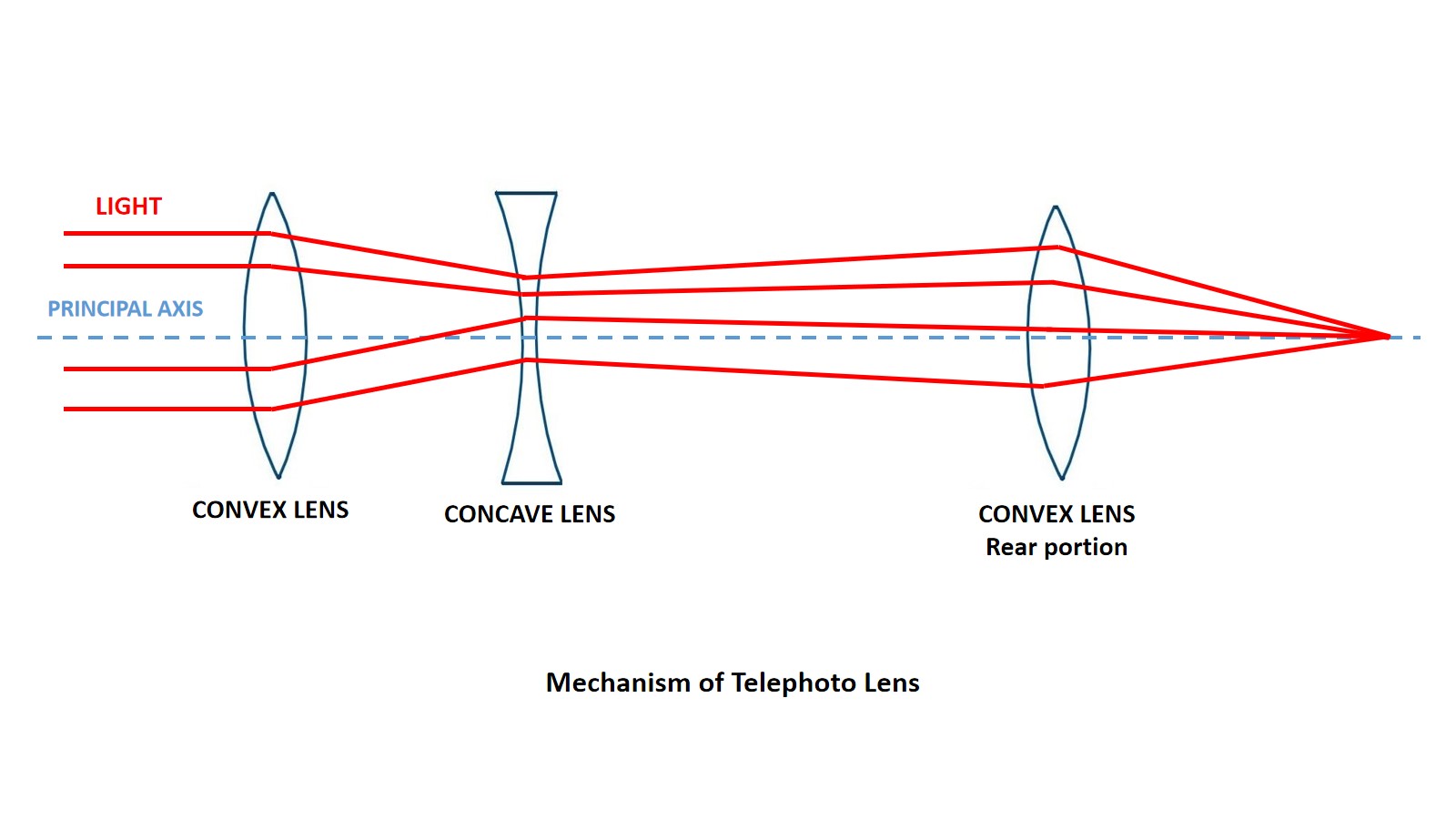
The lens makers installed another convex lens to the above combination. The frontal part of telephoto lens have convex and concave lens. These are responsible for magnifying the image and the rear convex lens converge the light. So, the magnified image is razor sharp.
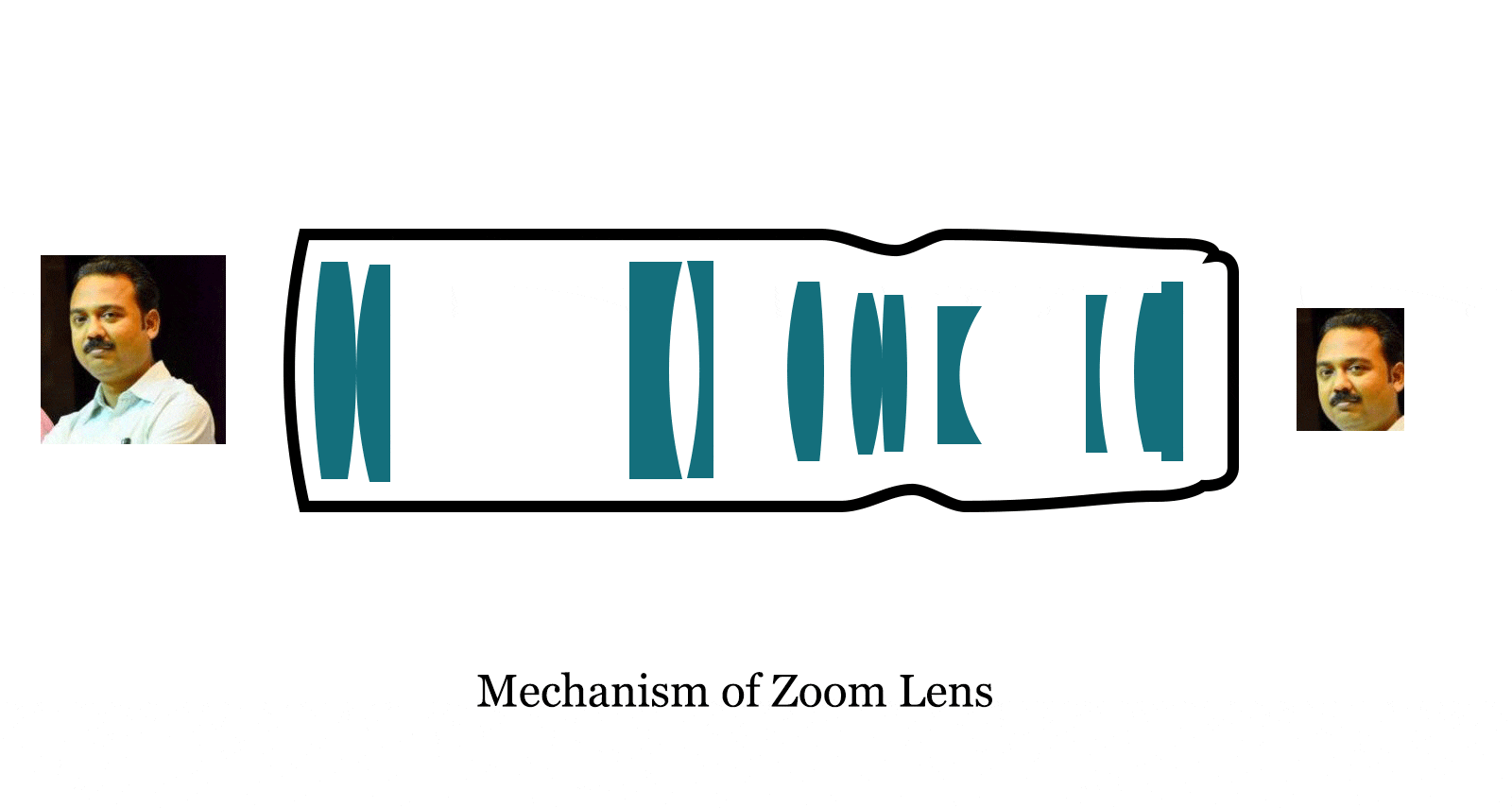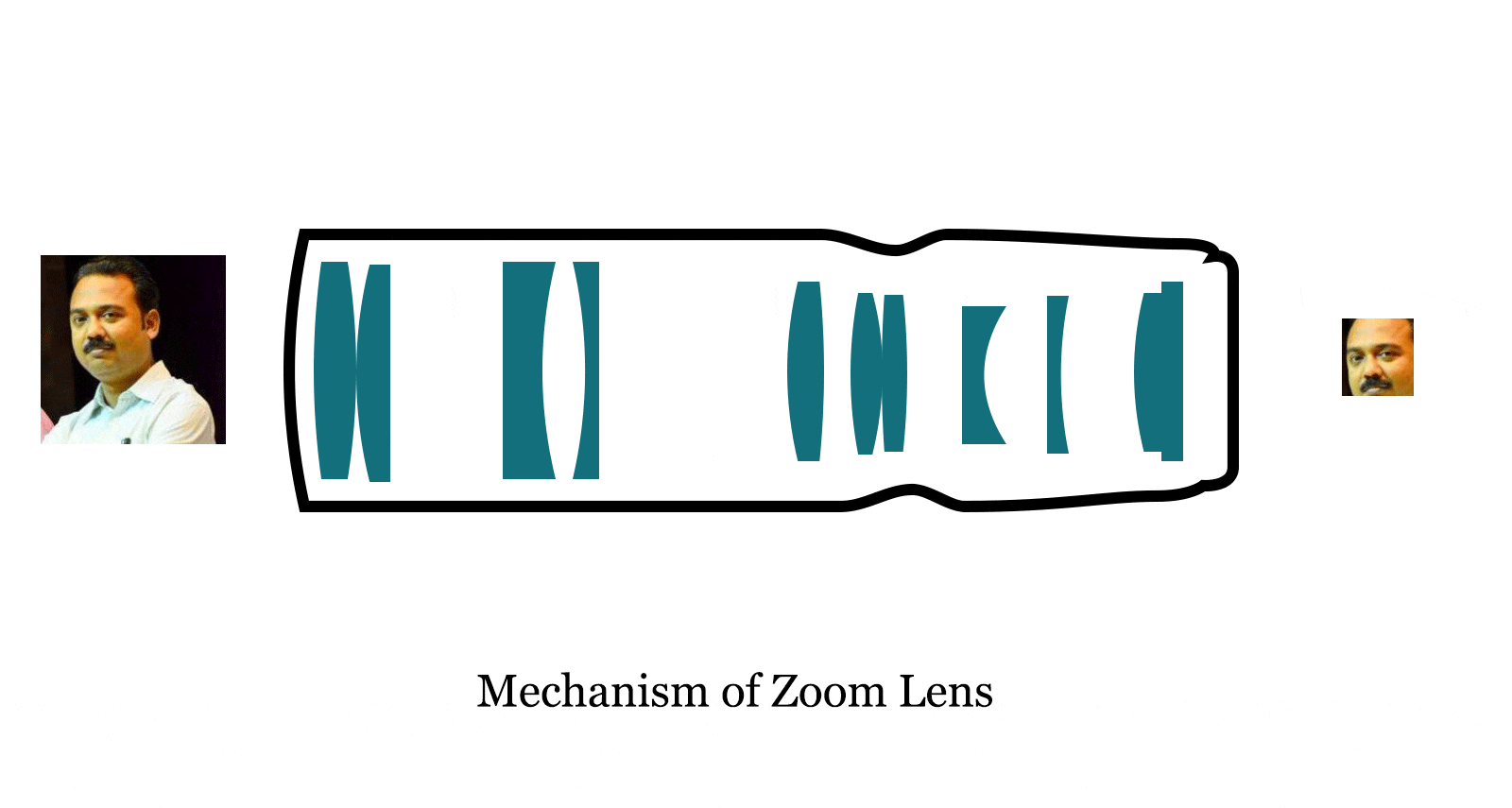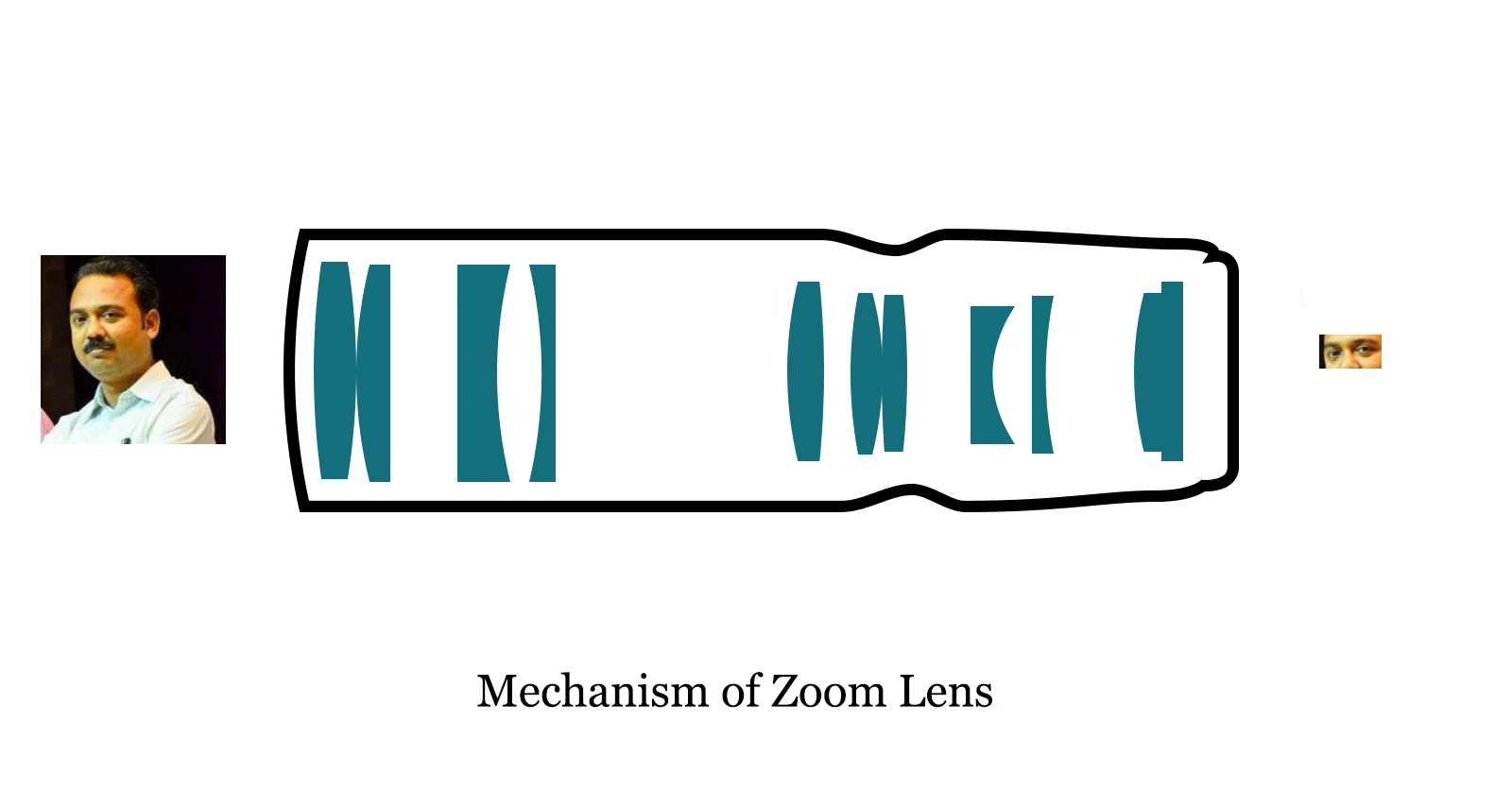
Two more convex and concave lens are used for adjusting the distance between the single concave and convex lens and zoom lens formed.
You may be interested to read other articles about unmasking the masked basics of photography.
Masked basics of photography – part I

Extremely interesting information Sir. Especially the comparison between Full-Frame and Crop censor.
It is an advanced course of basic photography, very informative, educational, tutorial.
Precious document indeed