100 photography tips can elevate your skills and enhance your understanding of your camera, regardless of whether you’re just starting out or have years of experience. This collection covers both technical knowledge and creative insights, offering detailed explanations, practical examples, and assignments for hands-on practice. Dive in to capture stunning images and refine your artistic vision!
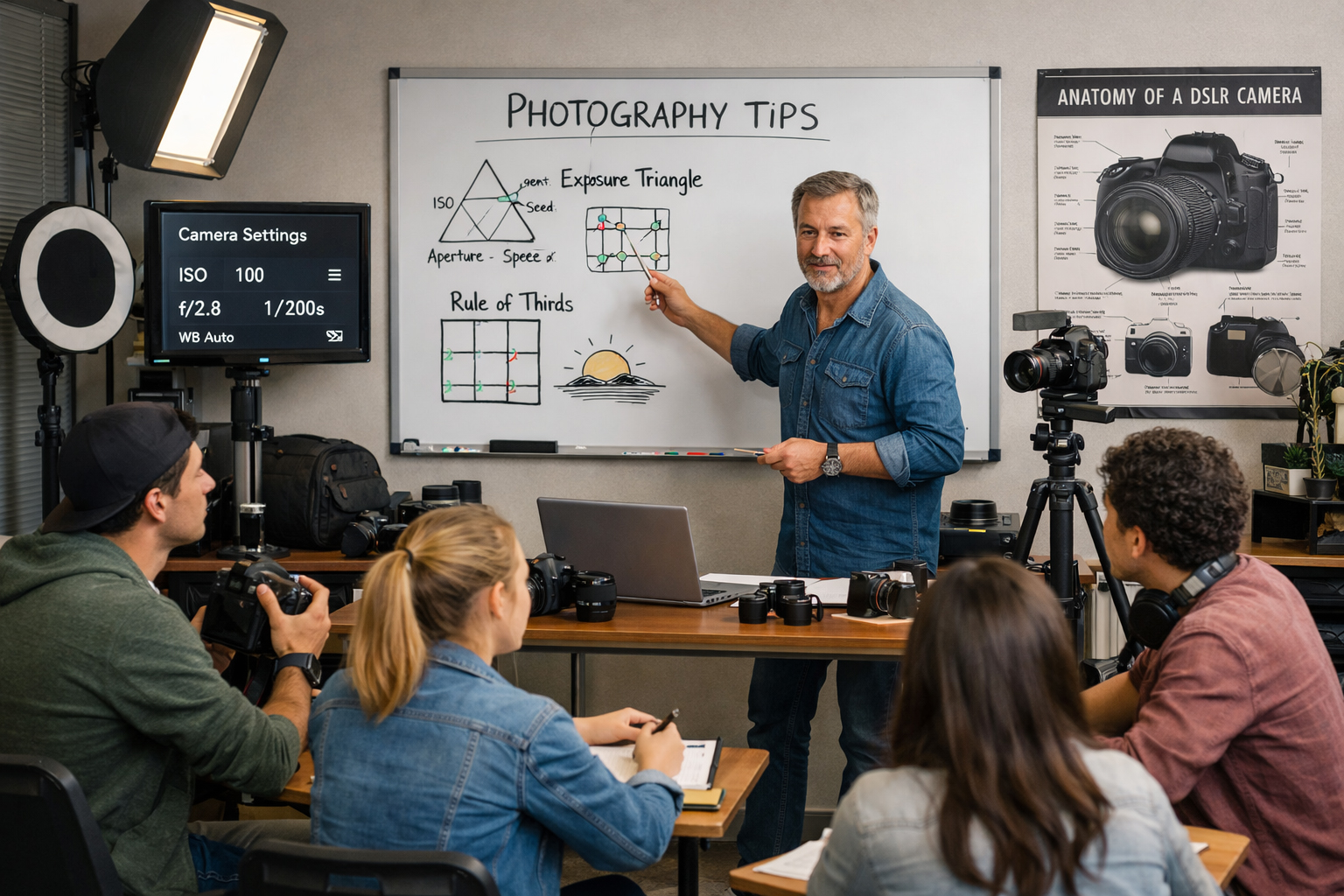

1. Understand the Exposure Triangle
Explanation:
The exposure triangle consists of aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. Understanding how these three elements interact is crucial for achieving the correct exposure in your photos.
Example:
A bright sunny day might require a low ISO (100), a fast shutter speed (1/1000s), and a wide aperture (f/2.8) to prevent overexposure.
Assignment:
Choose a scene and take three different photos by adjusting each component of the triangle while keeping the exposure consistent. Analyze how each change affects the image.
2. Master Composition with the Rule of Thirds
Explanation:
The rule of thirds involves dividing your frame into a 3×3 grid. Placing points of interest along these lines or at their intersections can create more balanced and dynamic compositions.
Example:
In landscape photography, you might place the horizon along the top third of the frame and a prominent tree at an intersection.
Assignment:
Take five photographs using the rule of thirds and compare them to images where you didn’t apply this rule. Evaluate which compositions are more compelling.
3. Utilize Leading Lines
Explanation:
Leading lines draw the viewer’s eye into the image, creating a sense of depth and guiding them to the focal point.
Example:
A winding road or a river leading to a mountain can effectively draw attention to the background.
Assignment:
Find a location with leading lines, such as a path or fence, and take a series of photos highlighting this technique.
4. Experiment with Depth of Field
Explanation:
Depth of field refers to the range of distance that appears sharp in your image. A shallow depth of field blurs the background, isolating the subject, while a deep depth keeps everything in focus.
Example:
For portraits, use a wide aperture (e.g., f/2.8) to create a soft, blurred background.
Assignment:
Take portraits using different apertures (f/2.8, f/5.6, f/11) and analyze how each affects the focus and feel of the image.
5. Explore Natural Light
Explanation:
Natural light changes throughout the day and can significantly impact your photography. Early morning and late afternoon (golden hour) offer soft, warm light ideal for most subjects.
Example:
A landscape shot taken during sunset will have a warm glow that enhances the scene.
Assignment:
Take photos at different times of the day and compare the effects of natural light on your subjects.

6. Master Framing Techniques
Explanation:
Framing involves using elements within your scene to create a “frame” around your subject. This technique can help focus attention and add depth.
Example:
Use branches or doorways to frame a person standing in a field.
Assignment:
Take three photos using different framing techniques and evaluate how they affect the viewer’s focus on the subject.
7. Use Negative Space
Explanation:
Negative space is the area surrounding your subject. It can enhance focus and create a minimalist aesthetic.
Example:
A lone tree in an expansive field emphasizes its isolation through negative space.
Assignment:
Create three images that effectively utilize negative space and analyze their visual impact.
8. Capture Motion with Panning
Explanation:
Panning involves moving your camera along with a moving subject, creating a sense of motion while keeping the subject sharp.
Example:
Track a cyclist as they pass by, resulting in a blurred background.
Assignment:
Practice panning with various moving subjects (cars, runners) at different speeds to master this technique.
9. Leverage Backlighting
Explanation:
Backlighting creates dramatic effects by positioning your subject against a light source, often resulting in beautiful silhouettes.
Example:
Photograph a person against a sunset for a striking silhouette.
Assignment:
Take silhouette photos at sunset or sunrise and experiment with different poses and angles.
10. Use Long Exposures
Explanation:
Long exposure photography captures motion over time, making it ideal for subjects like waterfalls or star trails.
Example:
Use a tripod to photograph a waterfall with a long exposure of several seconds to create a silky effect.
Assignment:
Experiment with long exposures in various environments and compare the results.
11. Incorporate Patterns and Textures
Explanation:
Patterns and textures add visual interest to your images, making them more engaging.
Example:
Capture the intricate patterns on a leaf or the texture of a brick wall.
Assignment:
Take close-up shots of various textures in your environment, focusing on light and shadow.
12. Focus on Eyes in Portraits
Explanation:
Sharp focus on the eyes creates a connection between the subject and the viewer.
Example:
Use a wide aperture to blur the background while ensuring the eyes are in sharp focus.
Assignment:
Capture five portraits, ensuring the eyes are always the focal point. Compare the emotional impact of each.
13. Take Advantage of the Golden Hour
Explanation:
The golden hour occurs shortly after sunrise and before sunset when the light is soft and golden, providing ideal conditions for photography.
Example:
Photograph landscapes or portraits during this time for flattering light.
Assignment:
Plan a photo shoot during the golden hour and compare your results to those taken in harsh midday light.
14. Experiment with HDR Photography
Explanation:
High Dynamic Range (HDR) photography combines multiple exposures to capture a wider range of light, ideal for high-contrast scenes.
Example:
Photograph a sunset with three shots at different exposures and merge them in post-processing.
Assignment:
Create an HDR image from a scene with high contrast, comparing it to a standard shot.
15. Capture Candid Moments
Explanation:
Candid photography captures spontaneous moments, revealing authentic emotions.
Example:
Document a child’s reaction while playing or interacting with others.
Assignment:
Spend a day capturing candid moments in a public place, focusing on expressions and interactions.

16. Utilize Color Theory
Explanation:
Understanding color relationships can enhance your compositions and evoke emotions. Complementary colors can create striking contrasts.
Example:
A vibrant red flower against a green background can create an eye-catching image.
Assignment:
Create a series of images showcasing different color combinations, experimenting with harmony and contrast.
17. Create Beautiful Bokeh
Explanation:
Bokeh refers to the quality of the out-of-focus areas in a photo, adding artistic flair and emphasizing the subject.
Example:
Photograph holiday lights with a shallow depth of field to create a pleasing bokeh effect.
Assignment:
Experiment with different backgrounds and light sources to achieve unique bokeh effects in your images.
18. Master White Balance
Explanation:
White balance adjustments can dramatically affect the mood and tone of your photos, making colors appear more natural.
Example:
Use a warmer setting for indoor shots with artificial light to avoid bluish tones.
Assignment:
Take the same photo with various white balance settings and compare the results.
19. Use Filters Wisely
Explanation:
Filters can enhance or alter your images. Common types include polarizing filters to reduce glare and neutral density (ND) filters to allow for longer exposures.
Example:
A polarizing filter can enhance the color of the sky and reduce reflections on water.
Assignment:
Experiment with at least two types of filters and evaluate their effects on your images.
20. Utilize a Tripod
Explanation:
A tripod stabilizes your camera, ensuring sharper images, especially in low light or long exposure situations.
Example:
Always use a tripod for night photography or landscape shots with slow shutter speeds.
Assignment:
Take a series of photos with and without a tripod, comparing sharpness and clarity.
21. Capture Reflections
Explanation:
Reflections can add depth and symmetry to your images, creating visually appealing compositions.
Example:
Photograph a city skyline reflected in a calm lake.
Assignment:
Find various reflective surfaces (water, glass) and capture creative reflections in your photography.
22. Focus on Details
Explanation:
Close-up shots of small details can reveal beauty often overlooked, adding depth to your portfolio.
Example:
Capture the intricate details of a flower or the texture of an object.
Assignment:
Take macro shots of different subjects, focusing on details and textures.
23. Use High and Low Angles
Explanation:
Shooting from different heights can create unique perspectives and add interest to your compositions.
Example:
Capture a landscape from a hilltop or shoot a portrait from below to emphasize your subject.
Assignment:
Take a series of photos from high and low angles and compare their impact on the viewer.
24. Explore Night Photography
Explanation:
Nighttime offers unique opportunities with lights and stars, presenting different challenges and aesthetics.
Example:
Use long exposures to capture star trails or cityscapes illuminated by streetlights.
Assignment:
Experiment with night shots, adjusting your settings to achieve the best results.
25. Incorporate Human Elements
Explanation:
Adding people to your landscape shots can provide context, scale, and emotional depth.
Example:
Include hikers in a scenic mountain photo to illustrate the grandeur of the landscape.
Assignment:
Take landscape photos with and without human elements, analyzing the differences in mood and scale.

26. Use Softboxes for Portraits
Explanation:
Softboxes diffuse light for flattering portrait photography, minimizing harsh shadows.
Example:
Position
a softbox at a 45-degree angle to your subject for even lighting.
Assignment:
Take portraits using natural light, then replicate the setup with a softbox to compare the results.
27. Capture Textures in Nature
Explanation:
Nature offers an array of textures, from rough bark to smooth stones, adding interest to your photographs.
Example:
Photograph tree bark or a close-up of a rock to highlight textures.
Assignment:
Create a series of nature shots focusing on textures, experimenting with lighting and angles.
28. Use Creative Cropping
Explanation:
Cropping can dramatically change the composition and focus of an image, emphasizing the subject.
Example:
Crop a wide landscape to highlight a particular feature, such as a mountain.
Assignment:
Take several photos and try different cropping options in post-processing to find the most impactful compositions.
29. Embrace Minimalism
Explanation:
Minimalism focuses on simplicity and reducing clutter in images, often leading to powerful compositions.
Example:
A single flower against a white background emphasizes its beauty without distractions.
Assignment:
Create a series of minimalist photos, focusing on single subjects with negative space.
30. Capture Your Surroundings
Explanation:
Documenting your immediate environment can lead to creative discoveries and unique narratives.
Example:
Take photos of local parks, streets, and community events, showcasing everyday life.
Assignment:
Create a photo essay capturing your neighborhood, focusing on details and storytelling.
31. Use Slow Shutter Speeds
Explanation:
Slow shutter speeds can create unique effects, such as blurring motion or light trails.
Example:
Capture the movement of clouds or the flow of water using long exposures.
Assignment:
Experiment with various shutter speeds in different environments to see how they affect motion capture.
32. Incorporate Natural Frames
Explanation:
Using natural elements (like trees or archways) to frame your subject can create more engaging compositions.
Example:
Photograph a person through a doorway or between branches to add depth.
Assignment:
Find locations with natural frames and create a series of images that highlight this technique.
33. Take Advantage of Local Markets
Explanation:
Local markets offer vibrant colors, interesting subjects, and candid moments to capture.
Example:
Photograph vendors, fresh produce, and interactions among shoppers.
Assignment:
Spend a morning at a local market, focusing on candid moments and vibrant colors.
34. Experiment with Abstract Photography
Explanation:
Abstract photography emphasizes shapes, colors, and forms rather than identifiable subjects, allowing for creative expression.
Example:
Capture the patterns in shadows or the play of light on surfaces.
Assignment:
Create a series of abstract images focusing on colors, patterns, and textures.
35. Use the Histogram
Explanation:
The histogram helps you evaluate the exposure of your image, showing the distribution of shadows, midtones, and highlights.
Example:
A well-balanced histogram will have data spread evenly across the spectrum.
Assignment:
Review the histograms of your photos and adjust your exposure settings based on what you observe.
36. Capture the Essence of Travel
Explanation:
Travel photography tells stories about places, cultures, and experiences.
Example:
Document local customs, street scenes, and iconic landmarks.
Assignment:
Create a travel photo essay that showcases your experiences in a recent trip.
37. Use Props Wisely
Explanation:
Incorporating props can add context and narrative to your photography.
Example:
A book in a portrait can reveal more about the subject’s personality.
Assignment:
Take a series of portraits incorporating different props and analyze how they change the story.
38. Create Photo Stories
Explanation:
Photo stories allow you to convey a narrative through a series of images.
Example:
Document a day in the life of a local artisan through a sequence of photos.
Assignment:
Choose a subject and create a photo story that captures their daily routine.
39. Analyze Famous Photographers
Explanation:
Studying the work of established photographers can inspire and inform your own style.
Example:
Analyze the compositions and techniques of photographers like Ansel Adams or Dorothea Lange.
Assignment:
Choose a photographer and create a photo series inspired by their style or techniques.
40. Capture Architectural Wonders
Explanation:
Architectural photography showcases the beauty of structures and design.
Example:
Photograph a local landmark, paying attention to lines and angles.
Assignment:
Create a series of architectural photos in your city, experimenting with perspective and lighting.
41. Utilize Shadows Creatively
Explanation:
Shadows can add depth, texture, and interest to your images.
Example:
Capture long shadows during golden hour to create dramatic compositions.
Assignment:
Take photos focusing on shadows, experimenting with different times of day for varied effects.
42. Document Changes Over Time
Explanation:
Capturing the same scene over time can highlight changes in nature, architecture, or your own life.
Example:
Document a building under construction or a tree changing with the seasons.
Assignment:
Choose a subject to photograph over time, creating a visual timeline.
43. Explore Double Exposure Techniques
Explanation:
Double exposure combines two images into one, creating ethereal and artistic effects.
Example:
Overlay a portrait with a landscape for a dreamy look.
Assignment:
Experiment with double exposure techniques in-camera or during post-processing.
44. Capture Cultural Diversity
Explanation:
Documenting different cultures can enrich your portfolio and provide meaningful narratives.
Example:
Photograph local festivals, traditional dress, or customs unique to a culture.
Assignment:
Create a photo series that explores cultural diversity in your community.
45. Experiment with Color Grading
Explanation:
Color grading in post-processing can dramatically alter the mood and aesthetic of your images.
Example:
Apply warm tones for a nostalgic feel or cool tones for a serene vibe.
Assignment:
Take a series of images and experiment with different color grading techniques in post-processing.

46. Learn to Use Your Camera’s Manual Mode
Explanation:
Manual mode offers complete control over exposure settings, allowing you to adapt to various situations.
Example:
Adjust settings based on changing light conditions for better results.
Assignment:
Spend a week shooting in manual mode, keeping a journal of your settings and the outcomes.
47. Capture Emotion in Portraits
Explanation:
Emotion can create powerful connections in portrait photography.
Example:
Capture genuine smiles, laughter, or thoughtful expressions.
Assignment:
Spend a day photographing people, focusing on capturing their emotions and expressions.
48. Master the Art of Self-Portraits
Explanation:
Self-portraits allow you to express yourself creatively and experiment with different styles.
Example:
Use mirrors or reflections to capture unique self-portraits.
Assignment:
Create a self-portrait series exploring different aspects of your personality.
49. Use Natural Elements in Your Compositions
Explanation:
Incorporating natural elements like flowers, leaves, or water can enhance your images.
Example:
Use petals in a portrait shoot for added interest and color.
Assignment:
Create a series of images that include natural elements as key components.
50. Explore Food Photography
Explanation:
Food photography captures the aesthetic appeal of dishes, often emphasizing color and texture.
Example:
Use natural light and simple backgrounds to highlight a beautifully plated meal.
Assignment:
Experiment with food photography, styling your dishes and capturing them in different settings.
51. Capture the Spirit of Sports
Explanation:
Sports photography captures the energy, motion, and emotion of athletic events.
Example:
Freeze a moment in a game, such as a soccer player scoring a goal.
Assignment:
Attend a local sports event and practice capturing the action and emotion of the game.
52. Use Split Toning in Post-Processing
Explanation:
Split toning allows you to apply different colors to the highlights and shadows of an image, adding mood and depth.
Example:
Apply warm tones to highlights and cool tones to shadows for a vintage look.
Assignment:
Experiment with split toning on different images to see how it alters the overall feel.
53. Capture the Seasons
Explanation:
Documenting seasonal changes can showcase the beauty of nature throughout the year.
Example:
Photograph the same tree in spring, summer, fall, and winter.
Assignment:
Create a seasonal photo series highlighting changes in your environment.
54. Use Environmental Portraits
Explanation:
Environmental portraits capture subjects in their surroundings, adding context to their character.
Example:
Photograph an artist in their studio to reflect their work and personality.
Assignment:
Take environmental portraits of different subjects, focusing on their interactions with their surroundings.
55. Explore Long-Term Projects
Explanation:
Long-term photography projects can deepen your skills and understanding of a subject.
Example:
Document a community initiative or personal journey over several months.
Assignment:
Choose a subject and commit to capturing it over a defined period, creating a cohesive body of work.

56. Experiment with Different Lenses
Explanation:
Different lenses provide unique perspectives and can greatly influence the mood of your images.
Example:
Use a macro lens for close-up shots or a wide-angle lens for expansive landscapes.
Assignment:
Experiment with at least three different lenses and evaluate the differences in your images.
57. Capture Street Life
Explanation:
Street photography captures the essence of daily life and candid moments in urban settings.
Example:
Photograph people interacting in a busy market or street scene.
Assignment:
Spend a day practicing street photography, focusing on candid moments and unique interactions.
58. Use a Color Wheel
Explanation:
A color wheel can help you understand color relationships and enhance your compositions.
Example:
Pair complementary colors for a striking visual impact.
Assignment:
Create a series of images that utilize different color schemes based on the color wheel.
59. Master the Art of Editing
Explanation:
Post-processing can enhance your images, allowing for adjustments in exposure, color, and sharpness.
Example:
Use software like Lightroom or Photoshop to edit and enhance your photos.
Assignment:
Edit a series of photos, experimenting with various adjustments and techniques to improve the final result.
60. Create Surreal Compositions
Explanation:
Surreal photography blends reality with imagination, creating dreamlike images.
Example:
Combine elements from different photos to create an otherworldly scene.
Assignment:
Develop a series of surreal images, experimenting with different concepts and editing techniques.
61. Capture Urban Landscapes
Explanation:
Urban landscape photography showcases the beauty of cities, architecture, and human interaction.
Example:
Photograph a bustling street or a quiet alley to capture the essence of urban life.
Assignment:
Create a series of urban landscape photos, exploring different areas and architectural styles.
62. Use the Fibonacci Spiral
Explanation:
The Fibonacci spiral is a composition technique that creates harmony and balance in your images.
Example:
Position your subject along the spiral’s curves to draw the viewer’s eye.
Assignment:
Take photos using the Fibonacci spiral as a guide for composition and analyze the results.
63. Capture Personal Milestones
Explanation:
Photographing personal milestones creates lasting memories and tells unique stories.
Example:
Document a family event, graduation, or a child’s birthday.
Assignment:
Create a photo series documenting a significant personal milestone.
64. Experiment with Different Styles
Explanation:
Exploring different photography styles can help you find your niche and develop your unique voice.
Example:
Try landscape, portrait, street, and abstract photography to see what resonates with you.
Assignment:
Create a portfolio showcasing your work in various styles.
65. Use Available Light Creatively
Explanation:
Utilizing available light can create stunning images without the need for artificial lighting.
Example:
Photograph a subject near a window to capture soft, natural light.
Assignment:
Experiment with available light in various settings and observe the effects on your photos.

66. Capture Local Wildlife
Explanation:
Wildlife photography allows you to explore nature and document animal behavior.
Example:
Photograph birds in a local park or animals in their natural habitats.
Assignment:
Spend time observing and photographing local wildlife, focusing on behavior and interactions.
67. Use Emotionally Charged Imagery
Explanation:
Images that evoke strong emotions can create powerful connections with viewers.
Example:
Capture moments of joy, sadness, or contemplation in your subjects.
Assignment:
Focus on photographing emotionally charged moments and analyze the impact of your images.
68. Experiment with Monochrome
Explanation:
Monochrome photography focuses on shades of one color, creating a timeless and classic feel.
Example:
Capture a scene in black and white to emphasize shapes and textures.
Assignment:
Create a monochrome series, exploring different subjects and compositions.
69. Capture Moments of Joy
Explanation:
Joyful moments create engaging and relatable photographs.
Example:
Document celebrations, laughter, or candid moments of happiness.
Assignment:
Spend a day capturing joyful moments in your life or in a public space.
70. Utilize Text Overlays
Explanation:
Adding text to your images can enhance storytelling and provide context.
Example:
Include quotes or captions that relate to the subject of your photo.
Assignment:
Create a series of images with thoughtful text overlays, focusing on how they complement the visuals.
71. Explore Vintage Photography Techniques
Explanation:
Vintage techniques can create unique aesthetics, evoking nostalgia.
Example:
Experiment with film photography or apply vintage filters in post-processing.
Assignment:
Create a series of images using vintage techniques or styles.
72. Document Personal Growth
Explanation:
Photography can capture your personal growth and changes over time.
Example:
Take self-portraits regularly to document your journey.
Assignment:
Create a visual diary of your personal growth, reflecting on the changes over time.
73. Experiment with Abstract Shapes
Explanation:
Abstract photography focuses on shapes and forms rather than recognizable subjects.
Example:
Capture patterns in architecture or nature that highlight their geometric aspects.
Assignment:
Create a series of abstract images exploring shapes and forms in your environment.
74. Use Natural Textures in Portraits
Explanation:
Incorporating natural textures can enhance the depth of your portraits.
Example:
Photograph a subject against a textured wall or with natural elements like leaves.
Assignment:
Experiment with different backgrounds and textures in portrait photography.
75. Capture Still Life Compositions
Explanation:
Still life photography allows for creative control over composition, lighting, and subject matter.
Example:
Arrange fruits or everyday objects in an aesthetically pleasing way.
Assignment:
Create a series of still life images, experimenting with different compositions and lighting setups.

76. Focus on Local Architecture
Explanation:
Documenting local architecture can showcase cultural heritage and design.
Example:
Photograph historic buildings or unique modern architecture in your area.
Assignment:
Create a photo series highlighting local architectural features and styles.
77. Use Dramatic Lighting
Explanation:
Dramatic lighting can create mood and tension in your images.
Example:
Use strong contrast between light and shadow to emphasize textures and shapes.
Assignment:
Experiment with dramatic lighting setups in your photography, analyzing the effects.
78. Capture the Essence of Friendship
Explanation:
Photographing friendships can reveal genuine emotions and connections.
Example:
Document friends engaging in activities together, showcasing their bond.
Assignment:
Create a series of images that celebrate friendship, focusing on candid moments.
79. Experiment with Negative Space in Still Life
Explanation:
Negative space in still life compositions can create balance and focus on the subject.
Example:
Position objects off-center, allowing for empty space to enhance the composition.
Assignment:
Create still life images utilizing negative space, analyzing their impact on the viewer.
80. Utilize Reflections in Water
Explanation:
Water reflections can create symmetrical and visually striking compositions.
Example:
Photograph a landscape reflected in a calm lake.
Assignment:
Explore locations with water and capture reflective images, focusing on symmetry and balance.
81. Document Cultural Festivals
Explanation:
Cultural festivals provide vibrant scenes filled with color, emotion, and community.
Example:
Capture the energy of a local festival, focusing on costumes and activities.
Assignment:
Attend a cultural event and document the experience through photography.
82. Create a Photography Blog
Explanation:
A photography blog allows you to showcase your work and share your journey.
Example:
Post images, stories, and insights about your photography experiences.
Assignment:
Start a photography blog, sharing your favorite images and experiences in the field.
83. Explore Wildlife Conservation Photography
Explanation:
Wildlife conservation photography raises awareness about environmental issues and species protection.
Example:
Document endangered species or local conservation efforts.
Assignment:
Create a photo series that highlights wildlife conservation efforts in your area.
84. Capture Architectural Details
Explanation:
Focusing on architectural details can reveal the craftsmanship and design of structures.
Example:
Photograph intricate carvings or unique features of buildings.
Assignment:
Create a series of close-up images highlighting architectural details in your community.
85. Use Time-Lapse Photography
Explanation:
Time-lapse photography captures changes over time, showcasing movement and transformation.
Example:
Document a sunset or flower blooming through a series of shots.
Assignment:
Create a time-lapse sequence of a natural event or daily activity.

86. Experiment with Composite Photography
Explanation:
Composite photography combines multiple images to create a single composition, allowing for creative storytelling.
Example:
Merge images of a subject with different backgrounds or elements.
Assignment:
Create a composite image using multiple photos, exploring surreal or imaginative themes.
87. Capture Street Performers
Explanation:
Street performers provide dynamic subjects filled with energy and emotion.
Example:
Document musicians, dancers, or artists performing in public spaces.
Assignment:
Spend time capturing street performers, focusing on their expressions and interactions with the audience.
88. Use the Golden Ratio
Explanation:
The golden ratio is a mathematical ratio that creates balance and harmony in compositions.
Example:
Position elements in your frame according to the golden spiral for a pleasing aesthetic.
Assignment:
Practice composing images using the golden ratio, analyzing the visual impact.
89. Capture Landscapes in Different Seasons
Explanation:
Documenting landscapes across seasons reveals the beauty of nature’s changes.
Example:
Photograph a landscape in spring bloom, summer green, autumn colors, and winter snow.
Assignment:
Create a seasonal landscape series, showcasing changes in a specific location.
90. Explore Underwater Photography
Explanation:
Underwater photography captures a unique world, offering opportunities for creativity and exploration.
Example:
Photograph marine life or underwater landscapes using specialized gear.
Assignment:
Experiment with underwater photography, focusing on composition and lighting in a new environment.
91. Utilize Smoke or Fog Effects
Explanation:
Smoke or fog can add mood and atmosphere to your images.
Example:
Capture a portrait with fog or smoke to create a mysterious effect.
Assignment:
Experiment with smoke or fog in your photography, focusing on creating a certain mood.
92. Capture Family Traditions
Explanation:
Documenting family traditions preserves memories and tells stories about your heritage.
Example:
Photograph holiday celebrations or family gatherings.
Assignment:
Create a
series that showcases your family’s traditions and the stories behind them.
93. Explore Aerial Photography
Explanation:
Aerial photography provides a unique perspective, showcasing landscapes and environments from above.
Example:
Use a drone to capture images of urban or natural landscapes.
Assignment:
Experiment with aerial photography, exploring different angles and perspectives.
94. Capture Emotion in Street Photography
Explanation:
Street photography can convey strong emotions, capturing candid moments of life.
Example:
Photograph individuals lost in thought or sharing a moment of joy.
Assignment:
Spend a day capturing emotional moments in public spaces, analyzing the reactions of your subjects.
95. Create a Photography Portfolio
Explanation:
A portfolio showcases your best work and represents your style.
Example:
Select images that highlight your strengths and unique approach.
Assignment:
Compile a portfolio of your favorite photographs, considering themes and techniques.

96. Explore Light Painting
Explanation:
Light painting involves using long exposure to create artistic effects with light sources.
Example:
Use a flashlight or sparklers to create shapes and patterns in the dark.
Assignment:
Experiment with light painting techniques, creating a series of images with different light sources.
97. Capture the Beauty of Abandoned Places
Explanation:
Abandoned places tell stories of history and decay, offering unique photographic opportunities.
Example:
Photograph an old building or a deserted location, focusing on textures and details.
Assignment:
Explore and document abandoned sites in your area, capturing their beauty and history.
98. Use Color Contrast
Explanation:
Color contrast enhances visual interest and draws attention to subjects.
Example:
Pair complementary colors to create vibrant compositions.
Assignment:
Create a series of images that explore color contrast and its impact on your photos.
99. Focus on Symmetry in Photography
Explanation:
Symmetry creates balance and harmony in compositions, drawing the viewer’s eye.
Example:
Photograph a reflection in water or a perfectly aligned architectural feature.
Assignment:
Capture images that highlight symmetry, experimenting with different subjects and compositions.

100. Create a Visual Diary
Explanation:
A visual diary allows you to document your life and experiences through photography.
Example:
Capture everyday moments that tell your story.
Assignment:
Keep a visual diary for a month, documenting daily experiences through photography.
This extensive list of photography prompts should inspire creativity and exploration in various aspects of photography. Enjoy your photographic journey!
** All images are generative AI
