Raster and vector methods are the two main ways digital images are stored and processed on computers, phones, and the web. These two methods work very differently, but both are essential in the digital world.
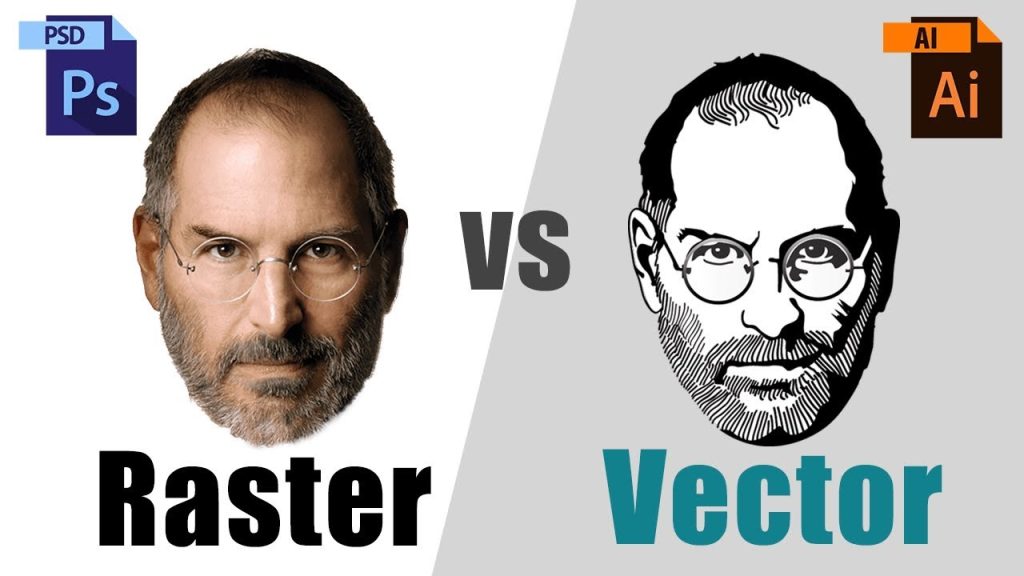
- Raster images are made of pixels—tiny colored squares that form a complete picture. They’re best for photos and detailed images.
- Vector images are created using mathematical paths. These are great for logos, icons, and graphics that need to be resized without losing quality.
Understanding the difference between raster and vector formats helps you choose the right one for your design, website, printing, or any digital media project. In this article, we’ll explore both methods in detail, with real-world examples and simple explanations.
What Is a Digital Image?
A digital image is a visual representation of a picture, drawing, or graphic that is stored as data on a computer. Every digital image must be stored in a format that a computer can read, display, and edit.
>>> You might be interested about digital image in depth <<<
There are two main ways to store and work with digital images:
- Raster Method
- Vector Method
Let’s take a closer look at each one.
1. Raster Image Method
What Is a Raster Image?
A raster image is made up of thousands (or millions) of tiny squares called pixels. Each pixel has a specific color, and when combined together, they form the complete image—like a mosaic or a grid of colored dots.
Examples of Raster Images:
- Photographs from a digital camera
- Web images (like JPEG, PNG)
- Scanned documents
- Social media graphics
Common Raster File Formats:
- JPEG (.jpg) – Used for photos, small file size
- PNG (.png) – Supports transparency, used for web
- GIF (.gif) – Used for simple animations
- TIFF (.tif) – High-quality format for printing
- BMP (.bmp) – Older format, not widely used today
Real-Life Example:
If you zoom in on a photo taken with your phone, you’ll start to see small square blocks. These are the pixels in a raster image.
Advantages of Raster Images:
- Great for detailed images like photos
- Supported by almost all devices and software
- Easy to edit using tools like Photoshop
Disadvantages:
- Lose quality when resized (become blurry or pixelated)
- Larger file size compared to vectors (especially in high resolution)
2. Vector Image Method
What Is a Vector Image?
A vector image is made using mathematical formulas to draw shapes, lines, and curves. It doesn’t use pixels. Instead, it stores instructions for how to draw each part of the image.
Because of this, vector images can be scaled to any size—large or small—without losing quality.
Examples of Vector Graphics:
- Logos
- Icons
- Text-based designs
- Illustrations and cartoons
Common Vector File Formats:
- SVG (.svg) – Used on websites and apps
- AI (.ai) – Adobe Illustrator format
- EPS (.eps) – Used in professional printing
- PDF (.pdf) – Can contain both vector and raster data
Real-Life Example:
Think of your company logo. If it’s a vector image, you can print it on a business card or a billboard, and it will still look sharp.
Advantages of Vector Images:
- Can be resized without losing quality
- Smaller file sizes for simple images
- Ideal for printing, logos, and technical illustrations
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for detailed photos
- Need special software to edit (e.g., Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape)
Raster vs Vector: Quick Comparison
| Feature | Raster | Vector |
|---|---|---|
| Made of | Pixels | Mathematical paths |
| File size | Usually larger (photos) | Smaller (for graphics) |
| Quality when resized | Becomes blurry | Stays sharp at any size |
| Best for | Photos, realistic images | Logos, icons, illustrations |
| Editing tools | Photoshop, GIMP | Illustrator, Inkscape |
When to Use Raster or Vector?
- Use raster when working with:
- Digital photography
- Web images with rich detail
- Social media graphics
- Use vector when creating:
- Logos or branding
- Icons and app graphics
- Print designs (posters, flyers)
Pro tip: Some design projects use both—a raster background with vector icons or text.
Bonus Tip
Sometimes, using a raster image is the most practical option—especially when working with photographs. Photos are naturally made up of many tiny details and color changes, which raster formats can capture accurately. Although you can convert a photo into a vector format, it often loses detail and ends up looking less sharp or realistic.
Final Thoughts
Both raster and vector methods have their place in digital image creation. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right format and tool for your project. If you’re working with detailed images or photos, raster is the way to go. If you need clean, scalable graphics like logos or illustrations, vector is the best choice.

