Now a days every DSLR is equipped with metering mode. It is also known as exposure metering or simply metering.
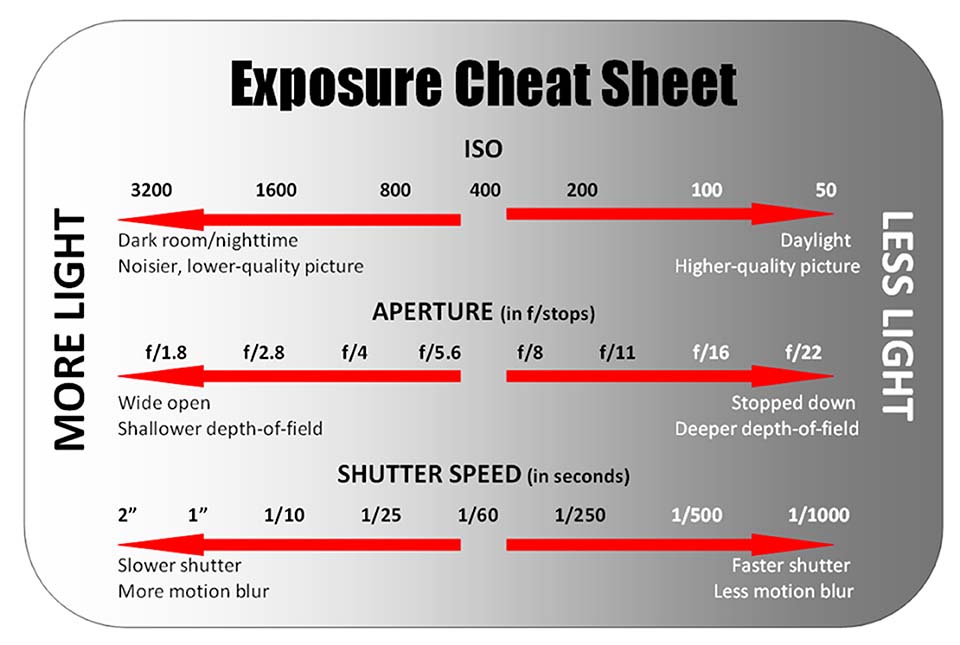
Metering is an auxiliary tool in camera to help the photo artist to control shutter speed, aperture, ISO for better quality of picture.
Back in the old days, there was no metering mode in SLRs. A manual-metering mode was used to get the perfect exposure for a subject. This tool measures the intensity of light and suggests the photo artists about aperture, shutter speed and so on.
Now a days this tool is integrated with the DSLR camera body for optimal exposure against a subject.
You can find the metering option from the viewfinder. It is always 0. zero tells the photo artists that the camera is ready with optimal exposure. To check the metering mode, change the DSLR into manual mode.
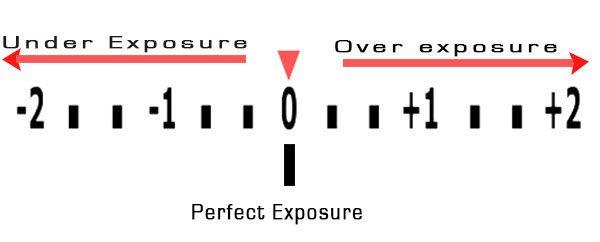
Now check the metering mode from the viewfinder. The viewfinder scale is moving. If photo artist moves the camera in a very bright area, metering bar moves into + (positive) position indicating that too much light for the current exposure setting. If the camera point to a dark side, then the metering scale goes to – (negative) side indicating that there is not enough light in current exposure setting.
In aperture priority, shutter priority or in scene mode, metering mode adjust the exposure automatically.
Metering mode can be classified into three prime categories. The following picture shows the meter modes in various DSLRs.
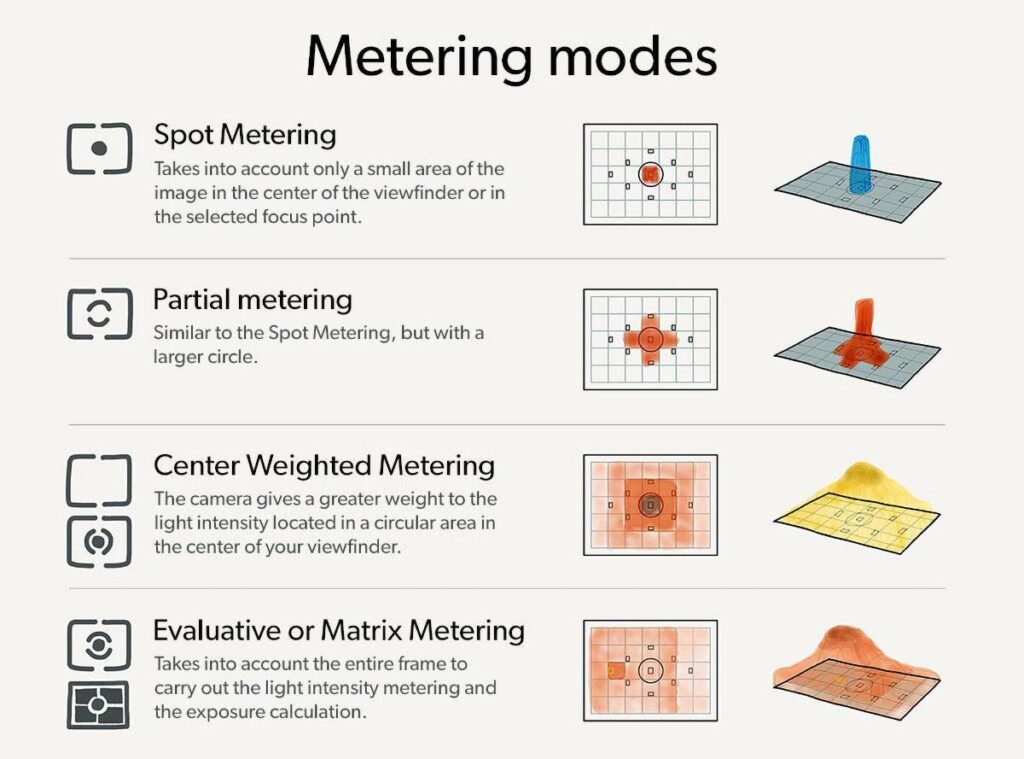
A) Matrix (Nikon) or Evaluative (Canon) metering: It is a by default mode for maximum DSLRs. It divides the frame into various zones and evaluates the light and dark. Now it sets the exposure based on the average light of this zonal system. This metering looks at where the photo artist focused within the frame and marks it more important than all other zones. I n matrix metering, every individual dark and light tone zone wise consisting with distance, color, subjects, highlights are responsible for optimal exposure. Instead of the above reasons many manufactures uses other information, which helps the exposure in perfect. For example, Nikon uses matrix-metering mode using a database of various pictures along with the zonal theory. This mode is very much used in landscape as well as portrait photography.
B) Centre weighted metering: It evaluates the light in the middle and its surroundings, ignoring the corners. This mode does not follow the specific focus point. It only evaluates the middle of the sensor. The subject which is in the middle of the frame can give the optimum result of exposure. This mode is very much helpful for close up shots. A head shot close up portrait which is behind the sun can dramatically gives optimal exposure of the close up portrait but the main disadvantage is the corner sides will be over exposed or wash out.
C) Spot metering: It evaluates only the small region or cell of the focused point. It is very much useful when the subject occupy a small area in a frame. It is not only measure the center of the frame but also other place of a frame. It is very much useful for bird photography. If a subject occupies a small area and sun behind it gives a good result for the subject rather than other two modes like matrix and center weighted. The previous two modes gives a silhouette image but spot meter gives a perfect result. Now a days Canon uses multi spot meter for a particular frame.
Another special metering mode is Partial metering. This mode is commonly available in Canon camera. This mode is weighted center and covers approximately 7% of the viewfinder area. It is working only on the center area. This metering mode is very much useful for over back-lit subject. It covers the subject in a very well manner and blown out the background. So, the best time to use partial metering mode is when the background is much brighter than the subject.
Summary:

The images are collected from internet.
