The mechanism of DSLR (Digital Single Lens Reflex) camera involves a series of steps to capture and process an image. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and their functions:
Light Enters the Lens
When you look through the viewfinder or the camera’s LCD screen, the lens is the primary element that allows light to enter the camera. The lens gathers and focuses light onto the camera’s image sensor.
Reflex Mirror
Inside a DSLR camera, there is a reflex mirror located between the lens and the image sensor. The reflex mirror is positioned at a 45-degree angle. Its purpose is to redirect the light entering the camera upwards toward the viewfinder.
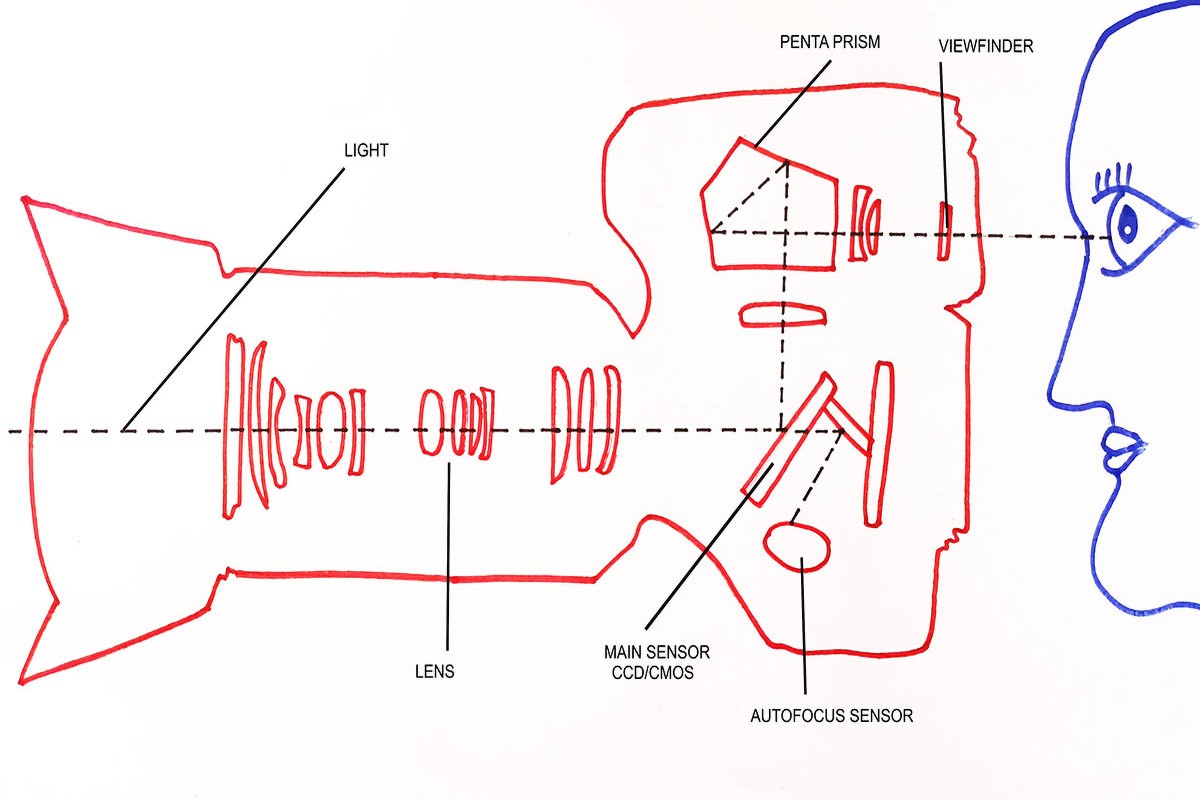
Viewfinder
The viewfinder is an optical component that allows you to see the scene you are about to capture. When light passes through the reflex mirror, it reflects off a focusing screen and enters the viewfinder, providing you with a real-time optical preview of the image.
Shutter
The shutter is a mechanism located in front of the camera’s image sensor. It controls the exposure time by briefly opening and closing to allow light to reach the sensor. When you press the shutter release button, the shutter opens, exposing the image sensor to light.
Image Sensor
The image sensor is the digital equivalent of film in a DSLR camera. It converts the incoming light into an electrical signal, which is then processed to create a digital image. DSLR cameras typically use either CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) or CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) sensors.
Autofocus System
DSLR cameras have autofocus systems that help in achieving sharp focus. The autofocus system uses sensors to detect contrast and analyze the sharpness of the image. It then adjusts the focus of the lens accordingly to ensure the subject is in focus.
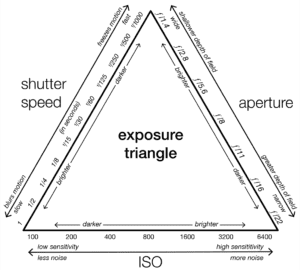
Exposure Control
DSLR cameras offer manual and automatic exposure control modes. In manual mode, you have control over settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO to determine the exposure. In automatic modes, the camera’s built-in light metering system measures the light and adjusts the exposure settings automatically.
Image Processing and Storage
After the light reaches the image sensor and the exposure is made, the captured image data undergoes processing. The camera’s image processor converts the raw data into a digital image by applying color correction, noise reduction, and other adjustments. The processed image is then stored in the camera’s memory card in a chosen file format (e.g., JPEG, RAW).
Display and Playback
DSLR cameras typically have an LCD screen on the back that allows you to review and preview images. The LCD screen also serves as a menu interface for accessing camera settings, playback, and image editing options.
Connectivity and Output
DSLR cameras provide various connectivity options, such as USB and HDMI ports, enabling you to transfer images to a computer or display them on external screens. Some models also offer wireless connectivity options like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth for easy image sharing and remote control.
The mechanism combines optical elements, mechanical components (such as the mirror and shutter), electronics, and image processing technology to capture high-quality digital images. Understanding these components and their functions helps photographers utilize the capabilities of DSLR cameras effectively.
