Understanding the intricate details of camera anatomy and the various accessories available can elevate your photography skills. Whether you’re a novice or an enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential components of a camera and the accessories that can enhance your photography experience.

Camera Anatomy
– Lens
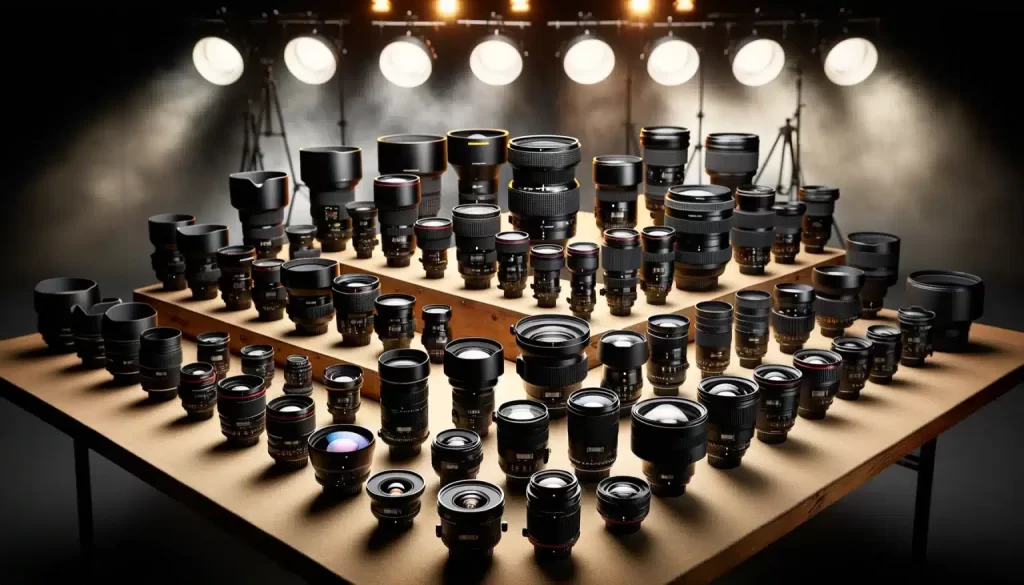

- The lens is the eye of the camera, capturing light and directing it to the sensor. Lenses vary in type and function:
- Prime Lenses: Fixed focal length, typically sharper and faster.
- Zoom Lenses: Variable focal length, versatile for different shooting scenarios.
- Macro Lenses: Designed for close-up photography.
- Telephoto Lenses: Long focal lengths for distant subjects.
– Body
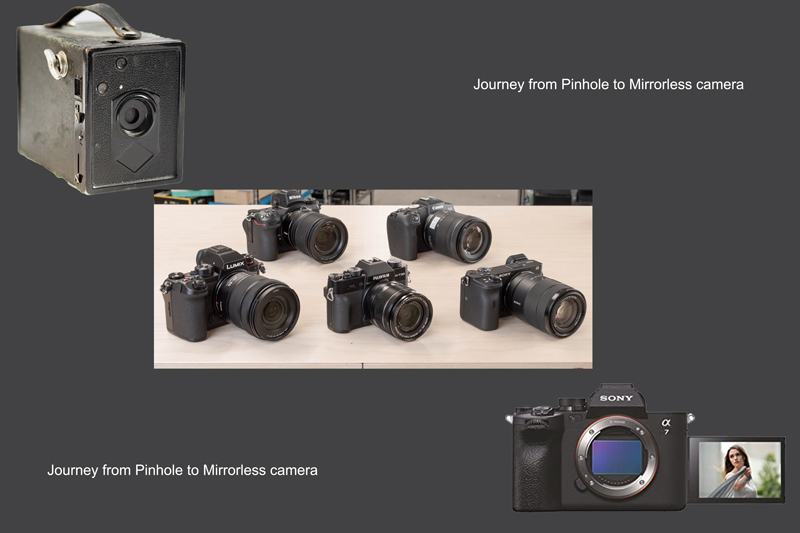

- The camera body houses all the internal components and provides the interface for user controls. It can be:
- DSLR (Digital Single-Lens Reflex): Uses a mirror mechanism to reflect light into an optical viewfinder.
- Mirrorless: No mirror mechanism; uses an electronic viewfinder or LCD screen.
– Sensor
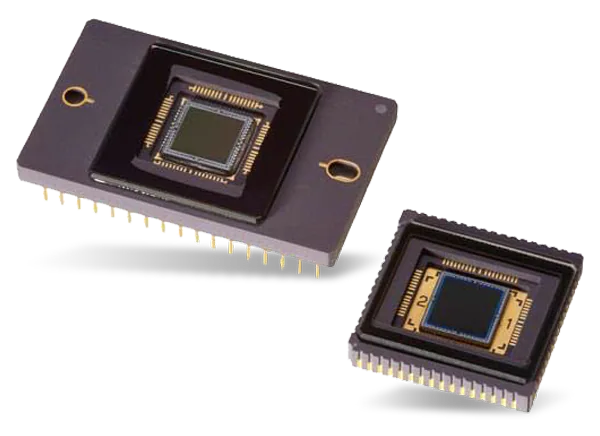
- The sensor captures light and converts it into an image. Sensor sizes include:
- Full-Frame: Equivalent to 35mm film; offers superior image quality and low-light performance.
- APS-C: Smaller than full-frame; common in consumer and prosumer cameras.
- Micro Four Thirds: Smaller still; used in compact and lightweight cameras.
– Viewfinder
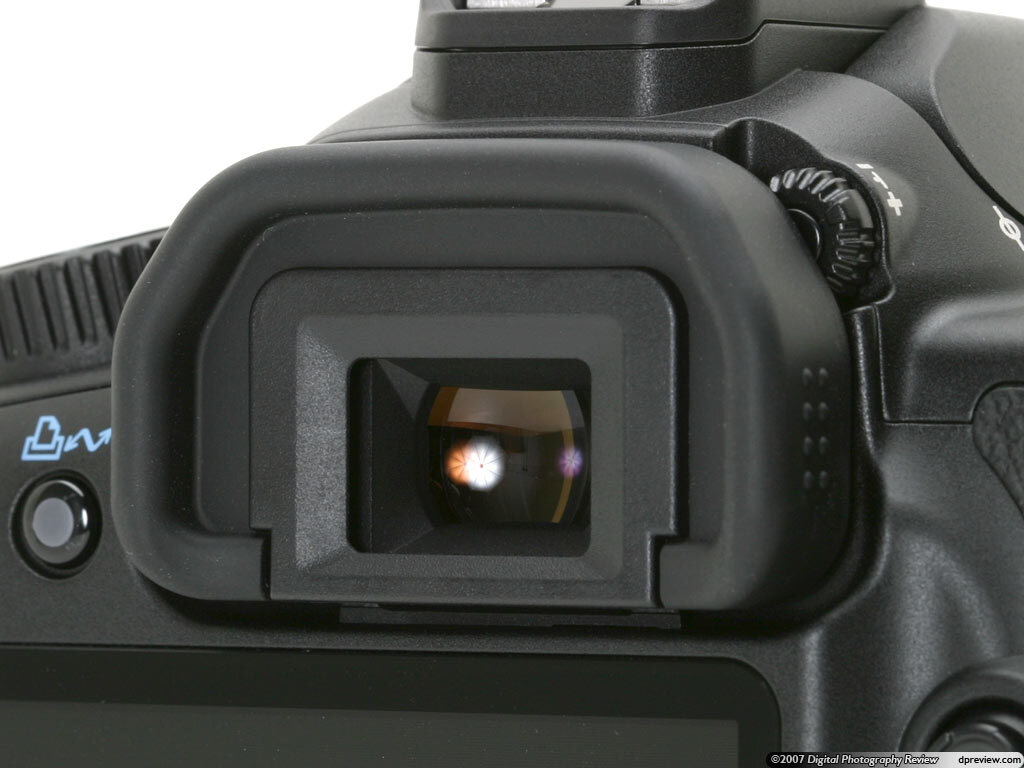

- The viewfinder is what you look through to compose your shot:
- Optical Viewfinder: Found in DSLRs, provides a direct optical view through the lens.
- Electronic Viewfinder (EVF): Found in mirrorless cameras, displays a digital image of what the sensor sees.
– Shutter
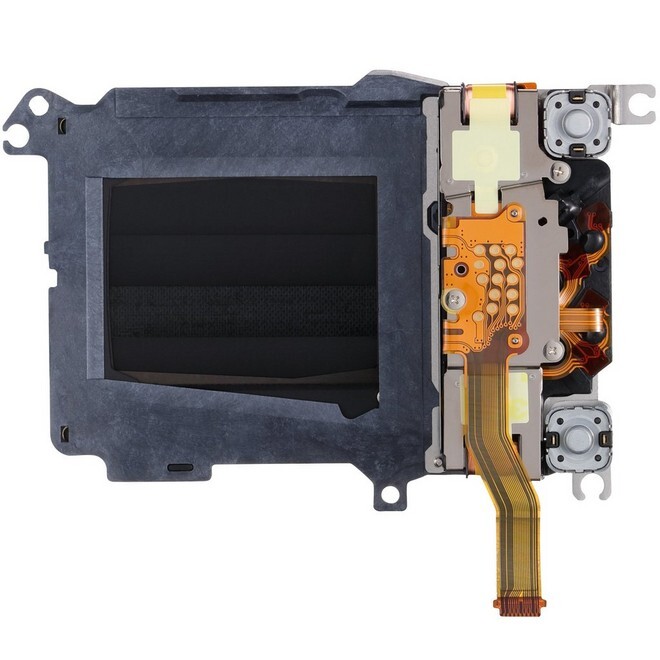
- The shutter controls the duration of light exposure to the sensor:
- Mechanical Shutter: Physical shutter that opens and closes.
- Electronic Shutter: Uses sensor readout to capture the image without moving parts.
– Aperture
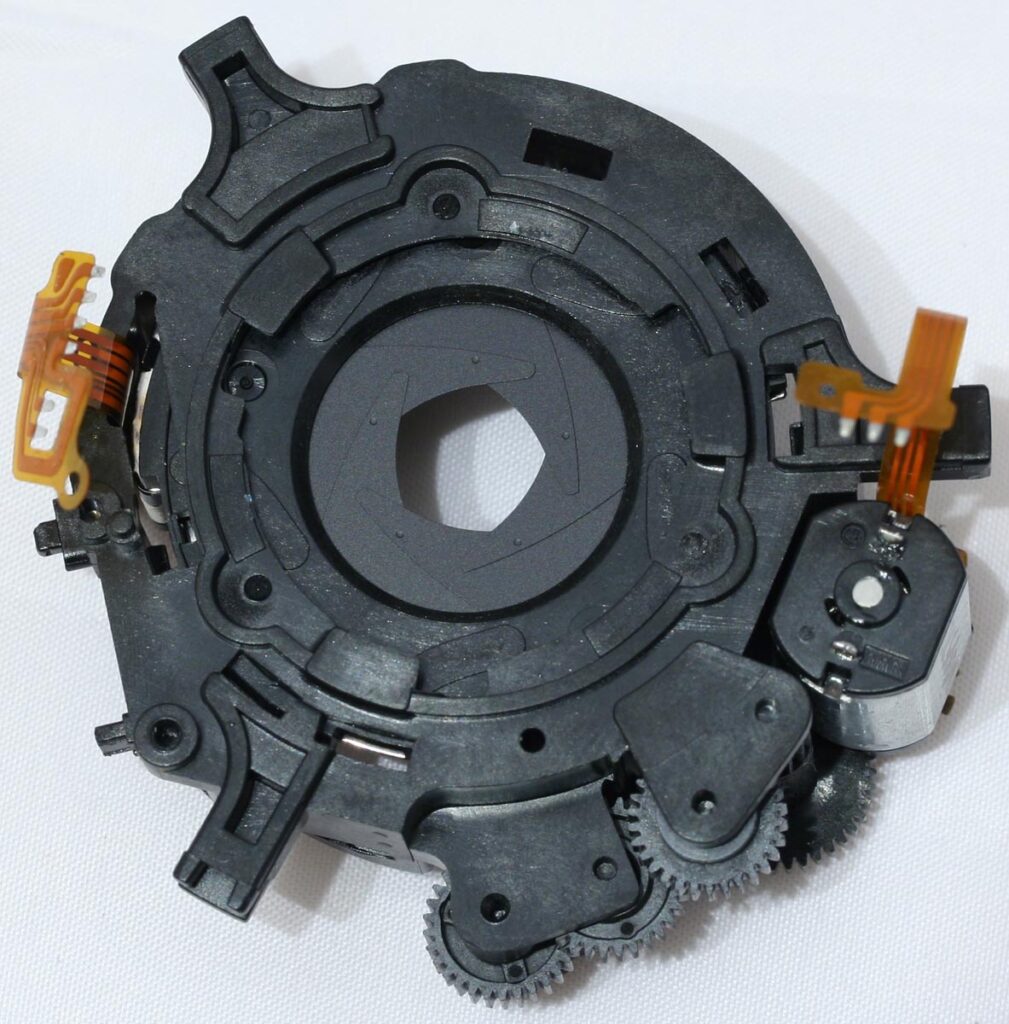

- The aperture is an adjustable opening in the lens that controls light entry and depth of field. It’s measured in f-stops (e.g., f/2.8, f/16).
– ISO
- ISO determines the sensor’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values (e.g., 1600, 3200) are useful in low light but can introduce noise.
– LCD Screen

- The LCD screen displays the live view, settings, and captured images. Some screens are touch-sensitive and can tilt or swivel.
– Image Processor
- The image processor handles data from the sensor and processes it into a usable image file. Faster processors enable quicker shooting and better image quality.
– Controls and Buttons
- Various buttons and dials allow you to adjust settings like shutter speed, aperture, ISO, and shooting modes.
Essential Camera Accessories
– Tripod

- A tripod provides stability, essential for long exposures, landscape photography, and video recording. Look for sturdy, lightweight options.
– Camera Bag
- A good camera bag protects your equipment and provides convenient access. Choose one with padded compartments and sufficient storage for your gear.
– Memory Cards

- Memory cards store your photos and videos. Opt for high-capacity, high-speed cards to ensure reliable performance.
– Extra Batteries

- Additional batteries are crucial for extended shoots, ensuring you don’t run out of power at critical moments.
– Lens Filters
- Filters attach to the front of your lens and offer various effects:
- UV Filters: Protect the lens from scratches and dust.
- Polarizing Filters: Reduce reflections and enhance colors.
- ND (Neutral Density) Filters: Allow for longer exposures in bright conditions.
– External Flash
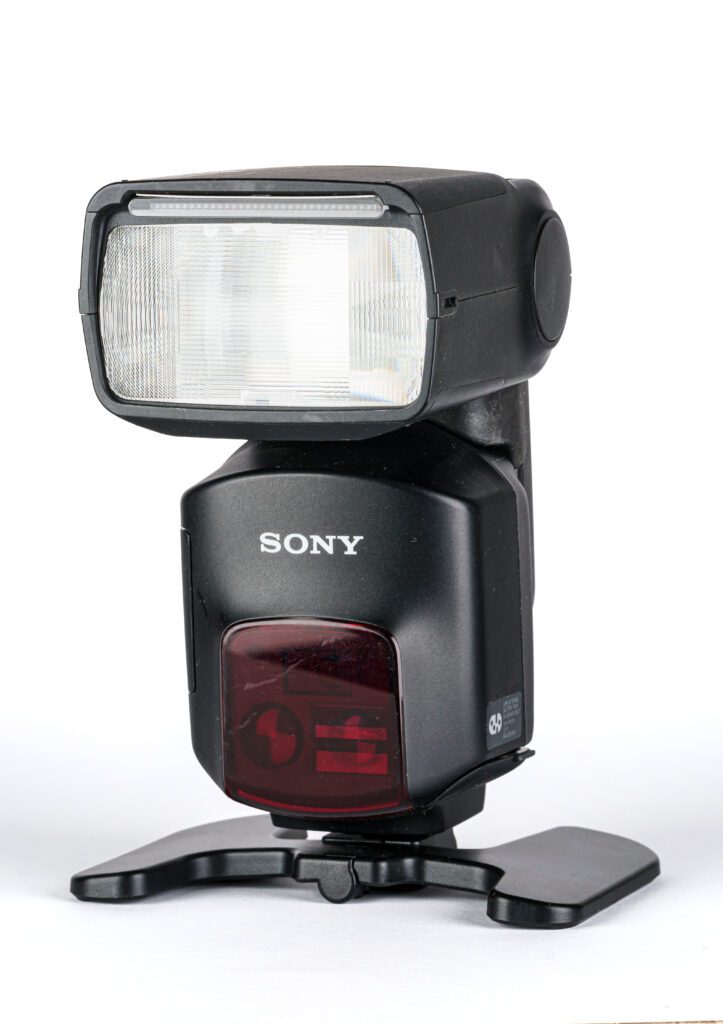

- An external flash provides more power and flexibility than the built-in flash. It’s essential for low-light situations and creative lighting techniques.
– Remote Shutter Release

- A remote shutter release allows you to take photos without touching the camera, reducing the risk of camera shake. It’s useful for long exposures and self-portraits.
– Cleaning Kit
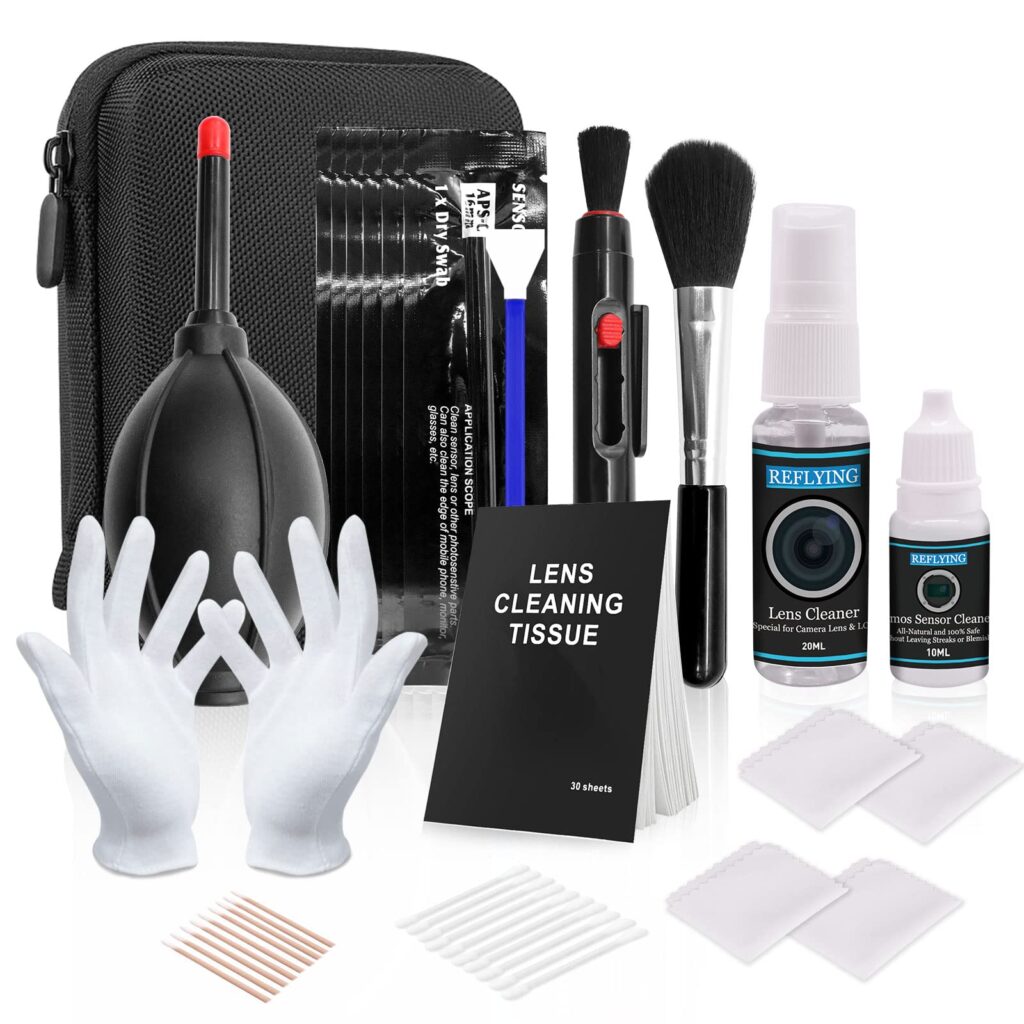

- A cleaning kit helps keep your camera and lenses free from dust and smudges. It typically includes a blower, brushes, lens cleaning solution, and microfiber cloths.
– Lens Hood
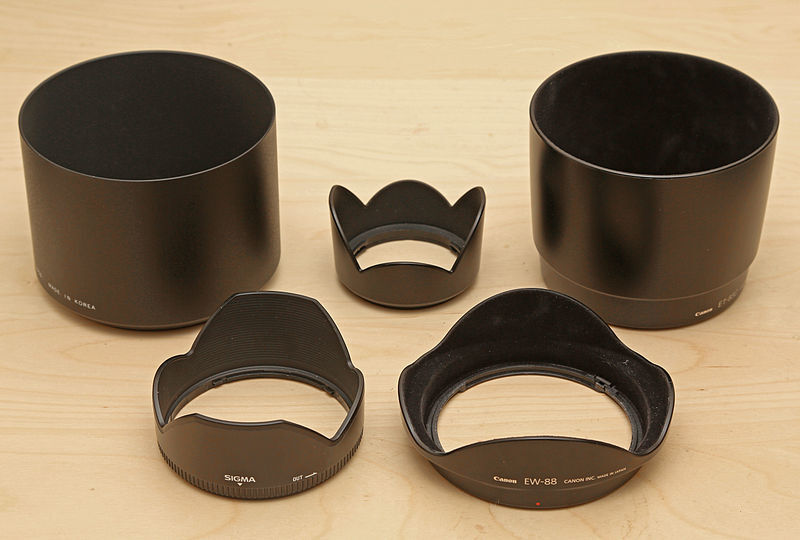

- A lens hood attaches to the front of your lens to block stray light and reduce lens flare, improving image contrast and color saturation.
– Camera Strap
- A comfortable camera strap makes it easier to carry your camera and prevents accidental drops. Choose a strap that distributes weight evenly.
Conclusion
A deep understanding of your camera’s anatomy and the right accessories can significantly improve your photography. From lenses and sensors to tripods and cleaning kits, each component and accessory plays a crucial role in helping you capture stunning images. Invest in quality gear and take the time to learn how each part works to enhance your photography skills.











